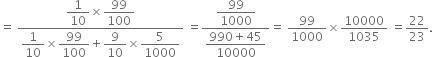Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeLet E1, E2, E be the events
E1 : ‘the person has the disease’
E2 : ‘the person is healthy’,
E : ‘test is positive’,
![]()
![]()
Required probability = ![]()
(By Bare's Theorem)