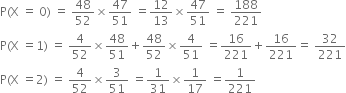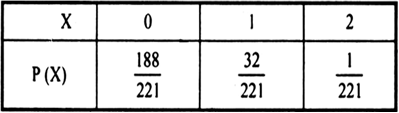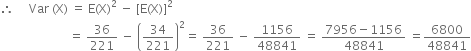980.
A class has 15 students whose ages are 14, 17, 15, 14, 21, 17, 19, 20, 16, 18, 20, 17, 16, 19, 20 years. One student is selected in such a manner that each has the same chance of being chosen and the age X of the selected student is recorded. What is the probability distribution of the random variable X ? Find mean, variance and standard deviation of X.
93 Views
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type