 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type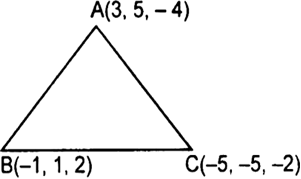
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeA line makes angles of 45° and 60° with the positive axes of x and y respectively. What angle does it make with the positive axis of z?
Find the length of the projection of the line segment joining the points P (3, -1, 2) and Q(2, 4, -1) on the line with direction ratios -1, 2, -2.
