 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeSolution not provided.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeIn the given Fig., ABC is a right triangle right angled at B. AD and CE are the two medians drawn from A and C respectively. If AC = 5 cm and ![]() find the length of CE.
find the length of CE.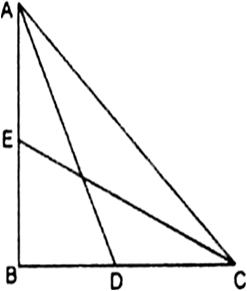
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type