Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type
AB is a line-segment. AX and BY are two equal line-segments drawn on opposite sides of line AB such that AX || BY. If AB and XY intersect each other at P. Prove that:
(i) ∆APX ≅ ∆BPY
(ii) AB and XY bisect each other at P.

 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeGiven: ABC is an equilateral triangle whose medians are AD, BE and CF.
To Prove: AD = BE = CF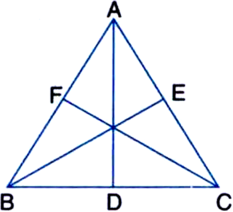
Proof: In ∆ADC and ∆BEC,
AC = BC
![]()
![]()
DE = EC
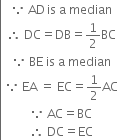
![]()
| SAS congruence rule![]()
![]() ....(1) | CPCT
....(1) | CPCT
Similarly, we can prove that
BE = CF ...(2)
and CF = AD ...(3)
From (1), (2) and (3)
AD = BE = CF
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type
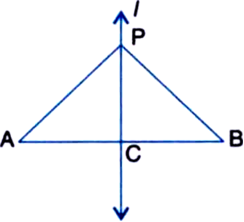
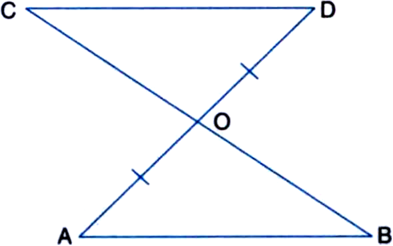
Line-segment AB is parallel to another line-segment CD. O is the mid-point of AD (see figure). Show that: (i) ∆AOB ≅ ∆DOC (ii) O is also the mid-point of BC.