 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsMatch the following Vir proteins with their correct function during Agrobacterium-mediated transfer of T-DNA to plant cells.
| Vir protein | Function |
| A. Vir G | i. Nucleus targeting of T-DNA |
| B. Vir D2 | ii. Component of membrane structure (transfer apparatus for T-DNA transfer. |
| C. Vir B1 | iii. Proteasome mediated destruction of proteins coating T-DNA complex. |
| D. Vir F | iv. Induction of Vir genes |
A - i; B - ii; C - iii; D - iv
A - iv; B - i; C - ii; D - iii
A - i; B - iii; C - iv; D - ii
A - iii; B - ii; C - i; D - iv
Some of the following transgenic approaches could be used for functional characterization of endogenous genes in plants:
A. Transformation using a binary vector containing a strong enhancer element and lacking the right border of T-DNA.
B. Transformation using a binary vector containing a promoter-less reporter gene sequence and a selection maker gene cassette within the T-DNA.
C. Transformation using a binary vector containing only a strong enhancer element and a selection marker gene cassette within the T-DNA.
D. Transformation using a binary vector lacking a reporter gene as well as both the left and right borders of T-DNA.
Which one of the following combinations can be used?
A and B only
B and C only
C and D only
A and D only
Transgenic tobacco plants over-expressing isopentenyl transferase (IPT) under the control of promoter region of Senescence Associated Receptor kinase (PSARK) were exposed to drought for 15 days followed by re-watering for 7 days. The following hypotheses were proposed regarding changes in the transgenic plants at the end of 7 days of re-watering:
A. The plants would be wilted and fail to survive.
B. The plants would be healthy and survive.
C. The plants would show higher production of cytokinin compared to wild type plants.
D. The plants would show higher production of abscisic acid compared to wild type plants.
Which one of the following combinations of the above hypotheses is correct?
A and C
A and D
B and C
B and D
With reference to plant biotic interactions, match the terms of column I with the most appropriate term of Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Phytoliths of Poaceae | i. Phloem feeders |
| B. Salicylic acid signalling pathway | ii. Decrease in stomatal aperture. |
| C. MAMP | iii. R genes/ NBS-LRR receptor |
| D. Effector-triggered immunity | iv. Mechanical barrier to herbivory |
A - ii; B - iv; C - i; D - iii
A - iii; B - i; C - ii; D - iv
A - iv; B - ii; C - iii; D - i
A - iv; B - i; C - ii; D - iii
D.
A - iv; B - i; C - ii; D - iii
The correct combination is-
A - iv; B - i; C - ii; D - iii
A researcher developed quadruple mutant that disrupted the function of all phytochrome interacting factor (PIF) family members. The following hypotheses were proposed regarding the phenotype of the mutant plants when grown in dark:
A. Plants would show short hypocotyls.
B. Plants would be etiolated.
C. Light induced genes would be activated.
D. The cotyledons would be open.
Which one of the following combinations of the above hypotheses is correct?
A, B, and C
A, B, and D
A, C, and D
B, C, and D
Identify the plant species from which artemisinin, an anti-malarial drug, is extracted.
Artemisia maritima
Artemisia scroparia
Artemisia annua
Cinchona officinalis
You have discovered a new transposon, TnX, and would like to identify its mode of replication. A heteroduplex of the TnX sequence is made with few mismatches and introduced into bacteria. The newly transposed genomic loci are sequenced. You find that the sequence of the transposon matched exactly with one of its parent strands. This suggests that
TnX transposes by conservative transposition mechanism.
TnX transposes using a site-specific recombination mechanism.
single strands of the duplex are inserted.
TnX transposes by replicative mechanism.
To assess the impact of a newly identified drug when added to a culture of sub-confluent HeLa cells, a researcher analyzes the fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) profile of untreated (-Drug) versus treated (+Drug) cells.
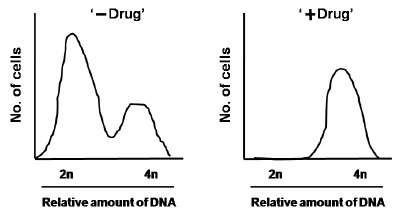
Based on the FACS profile shown above, this drug inhibits
G1 phase of the cell cycle
S phase of the cell cycle
G2/ M phase of the cell cycle
G0 phase of cell cycle
Oncogenic viruses could have either DNA or RNA genomes. Listed below are some oncogenic viruses (Column A), their genome types (Column B) and the cancers caused by these viruses (Column C).
| A | B | C |
| a. Hepatitis B | i. DNA | x. Burkitt's lymphoma |
| b. Epstein-Barr Virus | ii. RNA | y. T cell leukaemia |
| c. HTLV | z. Hepatocellular carcinoma |
Find out the correct combination.
(a) (i) (x); (b) (ii) (y); (c) (ii) (z)
(a) (ii) (y); (b) (i) (z); (c) (ii) (x)
(a) (ii) (y); (b) (ii) (z); (c) (i) (y)
(a) (i) (z); (b) (i) (x); (c) (ii) (y)
A uracil containing plasmid was constructed and was used in transformation into the wild type (ung’) and uracil-N-glycosylase mutated (ung’) E. coli cells and scored for transformants in the presence of appropriate antibiotics. Which one of the following statements correctly describes the experimental outcome?
ung’ cells will have fewer transformants compared to ung’ cells.
ung’ cells will give fewer transformants compared to ung’ cells
No transformants will be obtained in ung’ cells as uracil excision repair will not occur and the plasmid would not replicate.
Presence of uracil in DNA is unnatural and the plasmid DNA with uracils in it will not produce transformants in either ung’ or ung’ cells.
