 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsWhich of the following is an intracellular anchor protein?
Vitronectin
Vinculin
Integrin
Elastin
Out of the following matches of oncogenes with the proteins that each specifies, which one in incorrect?
erbA - thyroid hormone receptor
erbB - epidermal growth factor receptor
ras - guanine nucleotide binding protein with GTPase activity
fos - platelet-derived growth factor
After successive surgery and chemotherapy, the tumor of a breast cancer patient subsided. However, after almost 5 years, the tumor relapsed in a more aggressive manner and did not respond to the conventional chemotherapy delivered earlier. The following postulations were made.
A. Chemoresistant cells were persisting within the tumor even after therapy.
B. A population of quiescent cells existed, which under favourable conditions, transformed to new tumor cells.
C. High ABC (Atp-binding cassette)- transporter expressing cells persisted in the breast during chemotherapy.
D. Breast tumor cells which may have migrated to other tissues, returned to the breast immediately after chemotherapy was terminated.
Which of the above combination of statements is true?
A and D
A, B and C
Only B
B and D
Following are the experimental observations made on treatment of B cells:
A. Anti-immunoglobulin (anti-Ig) antibody treatment results in B cell apoptosis.
B. Anti-Ig plus CD40 ligand treatment results in B cell proliferation.
C. Anti-Ig plus CD40 ligand plus IL-4 treatment results in B cell proliferation and switching to IgG1.
D. Anti-Ig plus IL-4 treatment results in less B cell proliferation but switching to IgE.
From the above observation, which one of the following is the correct interpretation for the role of CD40 in B cell function?
Induce death of B cells.
Rescue B cells from death and Ig class switch to IgG1.
Inducing Ig class switch to IgE.
Induce Ig class switching to both IgG1 and IgE and inhibit B cell proliferation.
A potentially therapeutic approach for killing tumor cells without affecting normal is the use of immunotoxins. Immunotoxins constitute monoclonal antibodies against tumor cells conjugated to lethal toxins. Which of the following molecular approaches do you think is NOT appropriate for generating tumor-cell specific immunotoxins that will not kill normal cells?
Cell surface receptor binding polypeptide chain of toxin molecule should be replaced by monoclonal antibodies against a particular tumor cell type.
Constant region Fc domain of tumor cell specific monoclonal antibody should be replaced by ligation of toxins.
Variable region F(ab)2 domain of tumor cell specific monoclonal antibody should be replacedby ligation of toxins.
Inhibitor polypeptide chain of toxin should be conjugated to F(ab)2 domain of tumor cell specific monoclonal antibody.
Which of the following cellular communications shown below will override the process of normal development and lead to cancer?
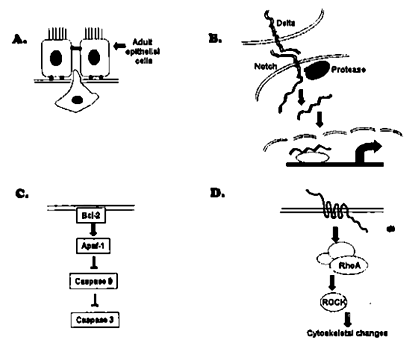
B and C
A and C
A and D
B and D
A major stimulus for spore formation in bacteria is
nutrition limitation
heat stress
cold stress
pH stress
ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters
Are all P-glycoproteins.
Are found only in eukaryotes.
Are both: a membrane-spanning domain that recognizes the substrate and an ATP-binding domain.
Affect translocation by forming channels.
Which of the following statements is INCORRECT in relation to the treatment of pre-B cells with phorbol esters?
Phorbol esters activate NFxB for translocation into the nucleus.
Phorbol esters activate protein kinase C.
Phorbol esters lead to phosphorylation of NF × B.
Phorbol esters remove the inhibitor from inactive NFxB complex in the cytoplasm
Mycobacterium tuberculosis is an intracellular bacterium. It prefers to infect
Macrophages
B-cells
T-cells
Neutrophils
A.
Macrophages
Mycobacterium tuberculosis is human-adapted and a prototypic intracellular pathogen of macrophages being the primary site for infection and disease.
