 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsJunctions which tether cytoskeletal filaments inside the cell are known as
anchoring junctions
occluding junctions
channel-forming junction
signal-relaying junctions
Which one of the following human serum immunoglobulins takes part in the classical complement fixation pathway?
IgD
IgE
IgA
IgG
A specific Mitogen Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) cascade comprising MEKK1 (a MAP3K), MKK1 (a MAP2K) and MPK6 (a MAPK) is activated sequentially in that order in Arabidopsis plants upon perceiving certain abiotic stress stimuli. The activated MPK6 phosphorylates and activates a transcription factor 'X', thereby making planttolerant to the abiotic stress. Two different variants of MKK1 protein, a kinase inactive (K1) and a constitutively active (CA) forms were expressed independently in mkk1 mutant Arabidopsis plant. Considering above facts, which one of the following statements is CORRECT?
'X' will be activated even in the absence of stimuli in CA plants.
'X' will not be activated in the absence of stimuli in CA plants.
'X' will be activated in the absence of stimuli in KI plants.
The KI plants will be tolerant to abiotic stress.
Which one of the following is the correct function of JAZ (JASMONATE ZIM-DOMAIN) protein family, a key regulator of Jasmonic Acid (JA) signalling response?
Binds to MYC2 and represses the JA dependent gene.
Binds to MYC2 and transcribes JA dependent genes.
Acts as receptor of JA signal.
Involved in directly inducing JA dependent genes.
To understand the microtubule-dependent motor activity of a freshly purified motor protein from budding yeast, a researcher set up microtubule-based gliding assay. In such an assay where microtubules are fluorescently tagged at its (+) end, the researcher observed that this motor protein moves the microtubule in the direction of its (+) end as shown below:

The newly identified motor protein is
Dynein
Myosin
Kinesin 1
Either Dynein or Kinesin 1
Major Histocompatibility complex(MHC) molecules are encoded by a cluster of genes called MHC locus. There are several reasons why an MHC molecule on the surface of a cell is important. Which one of the following reasons is INCORRECT?
To display self class I to demonstrate that the cell is normal and healthy.
To display foreign-peptide in class I to show that the cell is infected and to engage with T helper cells.
To display a self-peptide in class I and II to test developing T cells for autoreactivity.
To display a self-peptide in class I and II to maintain tolerance to self -proteins.
Two important features which aid the development of a tumor and its metastasis are epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and angiogenesis. A student testes four cell lines to determine capability by checking the expression the expression of VEGF-A, TWIST and Cyclin D1. Which one of the following figures is most likely to exhibit the characteristics of a highly cancer cell?
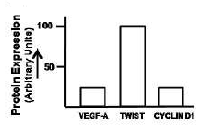
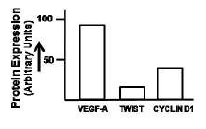
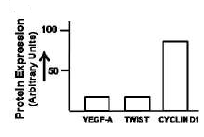
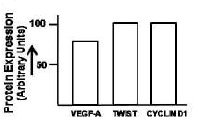
Two classes of genes - proto-oncogene and tumor suppressor gene usually contribute to the development of cancer. The following are some of the statements regarding both the genes.
A. Proto-oncogenes result in the development of cancer by gain-of-function mutation whereas tumor suppressor gene leads to cancer development by loss-of-function mutation.
B. Proto-oncogenes result in development in cancer by loss-of-function mutation whereas tumor suppressor gene leads to cancer development by gain-of-function mutation.
C. Mutation in both alleles of a protoncogene is required for induction of cancer whereas mutation in one of the two alleles in tumor suppressor gene is sufficient for promoting tumorigenesis.
D. Mutation in one of the two alleles in proto-oncogene is sufficient for induction of cancer whereas mutation in both the alleles of a tumor suppressor gene is required for promoting tumorigenesis.
Which combinations of the above statements are true for both the genes?
A and B
A and C
A and C
B and C
In a type of signal transduction pathway, ligand binding to a receptor triggers activation of a receptor-associated kinase. This kinase may be an intrinsic part of the receptor protein or tightly bound to the receptor. Receptors in which the tyrosine kinase is an intrinsic part of it's polypeptide chain is an intrinsic partof it's polypeptide chain are called the receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK). Which one of the following statements regarding RTK is INCORRECT?
All RTKs have three essential components: an extracellular domain containing ligand binding site, a transmembrane domain and a cytoplasmic segment that includes a domain with protein kinase activity.
Most RTKs are monomeric and ligand binding to the extracellular domain induces formation of receptor dimers.
All cytokine receptors belong to RTKs and cytokine binding activates tyrosine kinase and receptor dimerization.
Ligand binding to RTk leads to autophosphorylation of the protein tyrosine kinase in the cytoplasmic domain. The activated kinase then phosphorylates several tyrosine residues in the receptor's cytoplasmic domain.
C.
All cytokine receptors belong to RTKs and cytokine binding activates tyrosine kinase and receptor dimerization.
Among the given statements, statement 3 is the incorrect option.
The cell maintains a high concentration of protons inside the lysosome because of
antiporter in the lysosomal membrane
ATP-powered proton pump in the lysosomal membrane
facilitated diffusion proton channel in the lysosomal membrane
facilitated diffusion proton uniporter in the lysosomal membrane
