 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsCervical cancer-causing papilloma virus produces two oncoproteins E6 and E7 which are responsible for interfering with cell cycle regulation by
inactivating pRb and p53, respectively
modulating p53 and pRb, respectively
binding to cyclin D1 and CDK4
activating expression of p21
Which one of the following permits the rapid diffusion of small, water-soluble molecules between the cytoplasm of adjacent cells?
Tight junctions
Anchoring junctions
Adherens junctions
Gap junctions
Which one of the following is not true for alternative pathway of complement activation?
Alternative pathway uses the same membrane-attack complex as the classical pathway
Alternative pathway does not require antigen-antibody interactions.
Alternative pathway produces C3 by the same route as the classical pathway
Certain microbial surfaces have physicochemical properties that may result in activation of alternative pathway
C.
Alternative pathway produces C3 by the same route as the classical pathway
The alternative pathway provides an evolutionarily old and quite primitive innate immune defense mechanism. Activation begins with the C3 molecule. Native C3 contains an internal thiol ester in its a chain that, under normal physiologic conditions, undergoes continuous low-grade hydrolysis to create a “C3b-like” molecule, C3(H2O).
Brassinosteroids are a group of steroid hormones that function in a variety of cellular and developmental contexts in plants. Which one of the following acts as an inhibitor of the brassinosteroid receptor?
BRI 1
BKI 1
BAK 1
BSK 1
cAMP signalling plays a very important role in the development of Dictyostelium discoideum. Below are few statements related to it.
(a) Every amoeba at the time of aggregation has the potential to make, receive and relay cAMP.
(b) acb+ mutants develop normally but the spores formed appear glassy and are unable to germinate.
(c) The spores formed by the acg+ mutants germinate in the sorus itself.
(d) RegA is an extracellular phosphodiesterase.
(e) cAMP is continuously secreted in nanomolar amounts during aggregation.
Which combination of the above statements is correct?
(a) and (d)
(a) and (b)
(a) and (e)
(b) and (d)
Given below are the type of vaccination(column A), the diseases or conditions against which these vaccination type are used (column B) and the advantages or disadvantages for using thses vaccination types (column C).
| B | C | |
| (a) Live attenuated | (i) Rabies | (x) Strong immune response; |
| (b) Inactivated or killed | (ii) Measles | (y) Stable immune respons; cold chain is not required. |
| (c) Inactivated exotoxin | (iii) Diptheria | (z) Chance of untowards immunological reactions are very low;less successful in inducing long term immunity; need to be administered repeatedly |
Which one of the following combination is the most appropriate match?
(a0-9i)-(z), (b)-(ii)-(y), (c)-(iii)-(x)
(a)-(ii)-(x),(b)-(i)-(y),(c)-(iii)-(z)
(a)-(iii)-(y), (b)-(ii)-(x), (c)-(i)-(z)
(a)-(ii)-(z), (b)-(iii)-(x), (c)-(i)-(y)
G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are used to detect and respond to many to many different types of signals, including neurotransmitters, hormones involved in glycogen and fat metabolism and even photons of light. Which one of the folowing statements regarding GPCR is INCORRECT?
GPCRs are a large family with a common structure of seven membrane spanning α-helices.
GPCRs are coupled to trimeric G proteins comprising three subunits α,β and γ.
The Gα subunit is a GTPase switch protein that alternates between an active ('on') state with bound GTP and an inactive ('off') state with GDP.
The 'on' form gets bound to β and γ sub-units and acitvates a membrane-bound effector like adenylyl cyclase, phospholipase C or ion channel.
The following intracellular events occurs in a cell that is subjected that is subjected to conditions of starvation.
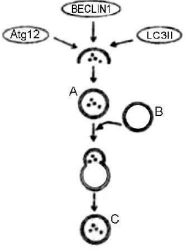
Which one of the following statements correctly represents the event shown above?
The cell is undergoing apoptotic cell death with the help of lysosomes (A).
The cell is undergoing autophagy by formation of autophagolysosomes (C).
The cell is undergoing necroptosis
The cell is undergoing autophagy and fusion occurs between lysosomes (A).
The extracellular matrix (ECM) is a complex combination of secreted proteins that is involved in holding cells and tissues together. The components of ECM form a network by binding to each other and communicate with cells by binding to adhesion receptors on the cell surface. ECM comprises mainly two classes of macromolecules, proteoglycans and very high molecular weight large proteins. Which one of the following statements regarding ECM constituents is INCORRECT?
Proteoglycans are a subset of secreted or cell surface-attached glycoproteins containing covalently linked specialized polysaccharide chains called glycosaminoglycans (GAGs).
GAGs are long branched polymers of specific repeating disaccharides of sialic acid and glucose or galactose.
Major types of GAGs present in ECM are heparan sulphate, chondroitin sulphate, dermatan sulphate, keratan sulphate and hyaluronan.
Major types of large proteins present in ECM are collagen, laminin, elastin and fibronectin.
Present-day cancer treatment uses many approaches. Beyond surgery and radiation treatment, which are most often employed in cases of larger, more discrete tumours, drug therapies can be used to target residual tumour cells and to attack dispersed cancers. Chemotherapies by anti-cancer drugs are mostly aimed at blocking DNA synthesis and cell division. A list of anti-cancer drugs is given in column A, their chemical nature in column B and their mechanism of action in column C.
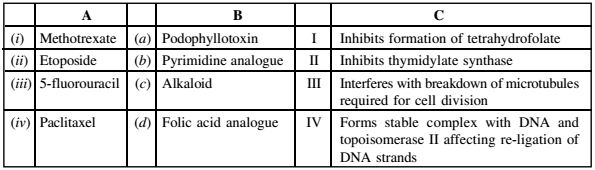
Which one of the following is the most appropriate match?
(i)-(a)-I, (ii)-(b)-II, (iii)-(c)-III, (iv)-(d)-IV
(i)-(b)-II, (ii)-(a)-III, (iii)-(d)-I, (iv)-(c)-IV
(i)-(c)-III, (ii)-(d)-IV, (iii)-(a)-II, (iv)-(b)-I
(i)-(d)-I, (ii)-(a)-IV, (iii)-(b)-II, (iv)-(c)-III
