 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsChromatin condensation is driven by protein complexes called condensins which are members of a family of "structural maintenance of chromatin" (SMC) proteins that play a key role in the organization of eukaryotic chromosomes. Condensins along with another family of SMC proteins called cohesins significantly contribute to chromosome segregation during mitosis. If the cells are treated with an inhibitor of cdk1 phosphorylation immediately before the cells enter M phase, which of the following statements is most likely to be true?
Sister chromatids are held together by condensins along the entire length of the chromosome.
Sister chromatids are held together by cohesins along the entire length of the chromosome.
Sister chromatids are held together by condensins and attached to each other only at the centromere.
Sister chromatids are held together by condensins and attached to each other only at the telomere.
B.
Sister chromatids are held together by cohesins along the entire length of the chromosome.
Among the given statements, statement 2 is likely to be true.
Estradiol synthesis follows a 2-cell-2-gonadotropin theory, where partial synthesis occurs in the granulosa cells and the rest in the theca interna cells of the Graffian follicle. Which one of the following correctly represents estradiol synthesis and secretion?
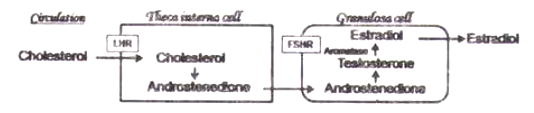
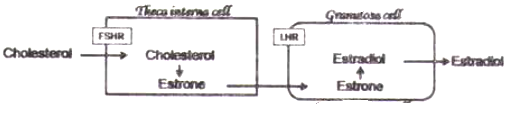
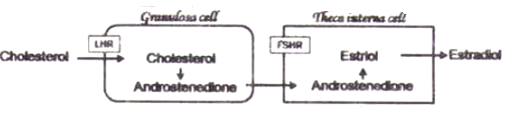
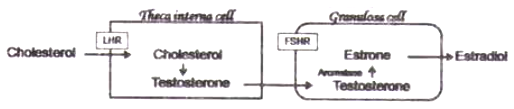
Which of the following gives the correct human disease-casual microbe match for each?
| Human Disease | Casual Microbe |
| A. Chronic gastritis | (i) Borrelia burgdorferi |
| B. Lyme disease | (ii) Helicobacter pylori |
| C. Scarlet fever | (iii) Rickettsia prowazekii |
| D. Typhus | (iv) Streptococcus pyogenes |
A - (ii); B - (i); C - (iv); D - (iii)
A - (ii); B - (iii); C - (ii); D - (iv)
A - (iv); B - (i); C - (ii); D - (iii)
A - (iv); B - (iii); C - (i); D - (ii)
In transgenic mice, the orientation and location of the loxP sites determine whether Cre recombinase induces a deletion, an inversion or a chromosomal translocation. If a researcher wants to put the loxP sites in such a manner that only inversion will take place, which one of the following construct best justifies their intention. Gene X is the target gene.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
The following diagram shows meiotic pairing in an inversion heterozygote and a point where single crossing over has occurred.
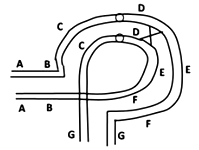
The resulting gametes produced may have
A. the chromosome having normal gene sequence.
B. the chromosome having inverted gene sequence.
C. a dicentric chromosome with duplication and deletion.
D. an acentric chromosome having duplication and deletion.
E. the chromosome having duplication and deletion.
Which of the following combination will be most appropriate for the diagram shown:
A, B, C, and D
A, B, and E
B, C, D, and E
A, C, D, and E
In an organism, expression of gene 'X' is induced in the presence of a hormone. Genetic analysis showed that the hormonal signal is transduced through two proteins Let 1 and Let 2. The expression of gene 'X' was studied in lines over-expressing (OE) the active Let proteins, knockout (KO) of the Let proteins or combination of both. Results of expression of gene 'X' in presence of the hormone is summarized below:
| Lines | Expression of Gene 'X' |
| WT | ++ |
| Let1 OE | ++++ |
| Let2 OE | ++++ |
| Let1 KO | - |
| Let2 KO | - |
|
Let1 OE Let2 KO |
- |
|
Let1 KO Let2 OE |
++++ |
Based on the above, which one of the following pathways best fits the observation made?
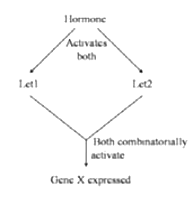
Hormone
Hormone
Hormone
Physical attachment between cells is very important in imparting strength in tissues. Various physical cell junctions in vertebrate epithelial tissues are classified according to their primary functions. Enlisted below in column A is the major function of a particular junction and column B enlists cell junctions, but not in the same order.
| Column A | Column B |
| A. Seals gap between epithelial cells. | i. Desmosomes |
| B. Connects acting filament bundle in one cell with that in the next cell. | ii. Hemidesmosomes |
| C. Connects intermediate filaments in one cell to those in the next cell. | iii. Tight junction |
| D. Anchors intermediate filaments in a cell to extracellular matrix. | iv. Adherens junction |
Choose the correct combination.
A - (i); B - (ii); C - (iii); D - (iv)
A - (ii); B - (iii); C - (iv); D - (i)
A - (iii); B - (iv); C - (i); D - (ii)
A - (iv); B - (i); C - (ii); D - (iii)
A hypothetical operon involved in the synthesis of an amino acid 'X' is 'ON' (transcribing) in the presence of low level of 'X' and 'OFF' (not transcribing) in presence of high level of 'X'. The symbols a, b, and c (in the table below) represents a structural gene for the synthesis of X (X-synthase), the operator region and gene encoding the repressor-but not necessarily in the order. From the following data, in which superscripts denote wild type or defective genotype, identify which are the genes for X-synthase, operator region and the repressor.
| Strain | Genotype | X-synthase activity in the presence of low level of 'X' | X-synthase activity in the presence of high level of 'X' |
| 1. | a-b+c+ | Detected | Detected |
| 2. | a+b+c- | Detected | Detected |
| 3. | a+b-c- | Not detected | Not detected |
| 4. | a+b+c+/ a-b-c- | Detected | Not detected |
| 5. | a+b+c-/ a-b-c+ | Detected | Not detected |
| 6. | a-b+c+/ a+b-c- | Detected | Detected |
The respective genes for 'X' synthase, the operator region and repressor are
a, b, c
c, a, b
b, c, a
b, a, c
The frequency of cells in a population that are undergoing mitosis (the mitotic index) is a convenient way to estimate the length of the cell cycle. In order to measure the cell cycle in the liver of the adult mouse by measuring the mitotic index, liver slices are prepared and stained to easily identify cells undergoing mitosis. It was observed that only 3 out of 25,000 cells are found to be undergoing mitosis. Assuming that M phase lasts 30 minutes, calculate the approximate length of the cell cycle in the liver of an adult mouse?
76 hours
50 hours
42 hours
21 hours
Which one of the following statements correctly applies to proteins which are translated on the rough endoplasmic reticulum?
Cytoplasmic proteins which are targeted to the nucleus in response to hormone stimuli.
Proteins targeted to lysosomes, plasma membrane and cell exterior.
Proteins that are targeted to the nucleus through endoplasmic reticulum lumen as the lumen is in direct connection with the intermembrane space of the nucleus.
All proteins which get targeted to peroxisomes.
