 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsThe genome of a bacterium is composed of a single DNA molecule which is 109 bp long. How many moles of genomic DNA is present in the bacterium? [Consider Avogadro No = 6 × 1023]
× 10-23
× 10-14
6 × 1014
6 × 10-23
A living cell has a protoplasm which is water based and demarcated by a lipid bilayer membrane. If a cell is pierced up to 5th of its diameter with a very sharp needle, after taking the needle out
no effect will be observed.
protoplasm will leak out from the hole made by the needle for a few minutes until the cell heals the wound.
protoplasm will keep on leaking out till the cell is dead.
the cell will burst like a balloon.
Transposons can be primarily categorized into two types. DNA transposons and reterotransposons. Given below is some information regarding the above.
A. Eukaryotic DNA transposons excise themselves from one place in the genome and integrate into another site.
B. Reterotransposons are RNA sequences that are first reverse transcribed into cDNA and then integrate into the genome.
C. Reterotransposons move by a copy and paste mechanism through an RNA intermediate.
D. As DNA transposons move via a cut and paste mechanism, there can never be an increase in the copy number of a transposon.
Which of the statement(s) is/are true?
A and C
B and D
B only
D only
A.
A and C
Among the given statements, statements A and C are true.
E. coli was grown in three different experimental conditions. In one, it was grown in medium containing glucose as a carbon source; in the second in medium containing both glucose and galactose; and in third was infected with phage. Match the curves shown below to the treatment.
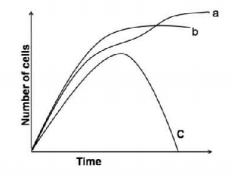
a is grown in glucose; b is grown in glucose and galactose; c is infected with phage.
a is grown in glucose and galactose; b in glucose; c is infected with phage
a is infected with phage; b is grown in glucose and galactose; c in glucose
a is infected with phage; b is grown in glucose; c in glucose and galactose
In a mitochondrial respiration experiment, a researcher observed the following profile of oxygen consumption upon addition of following compounds at times I, II, and III.
a. ADP + Pi
b. Dinitrophenol, an uncoupler
c. Oligomycin, an ATPase inhibitor
d. Cyanide
e. Succinate
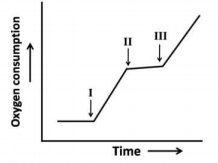
Which of the following describes the profile appropriately?
I - b; II - d; III - e
I - a; II - d; III - c
I - a; II - e; III - c
I - a; II - c; III - b
For a population growing exponentially with at a growth rate r, its population doubling time is
(N0 × 2)/ r
ln 2/r
λ ln w
ln r × 2
The transport of fructose into the enterocytes is mediated by:
sodium-dependent glucose transporter 1 (SGLT 1).
glucose transporter 5 (GLUT5).
SGLT 2
GLUT 4
Insulin increases facilitated diffusion of glucose in muscle cells by:
phosphorylation of glucose transporters.
containing endosomes into the cell membrane.
inhibition of the synthesis of mRNA for glucose transporters.
dephosphorylation of glucose transporters.
Which of the following bacteria has sub-cellular localization in lysosomes?
Salmonella typhi
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Vibrio cholerae
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Labelling of membrane-spanning domain of any integral membrane protein in a given plasma membrane vesicle (without disrupting its structure) is successfully carried out by
immunochemical methods
metabolic labelling with radioisotopes.
hydrophobic photoaffinity labelling
limited proteolysis followed by metabolic labeling
