 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsThe rank/ abundance plot given below illustrates three well-known species abundance curves (a, b, c)

Based on the shapes of the curves select the correct option.
a - exponential; b - log normal; c - geometric series.
a - broken stick; b - geometric series; c - log normal
a - broken stick;b - log normal; c - geometric series.
a - exponential; b - geometric series; c - log normal
In an intact cell patch-clamp experiment,
two electrodes are inserted into the cytosol but at different depths.
one electrode is applied to the plasma membrane in a region containing only lipids and one into the cytosol.
two electrodes are applied to the plasma membrane, one in a region containing only lipids and the other in a region containing one or few ion channels.
one electrode is applied to the plasma membrane containing one or few ion channels and one electrode inserted into the cytosol.
Given below are organelles (column A) and properties associated with the organelles (column B).
| Column A | Column B |
| A. Lysosomes | i. Anterograde transport from ER to Golgi |
| B. cis-Golgi | ii. CLathrin - coated vesicles |
| C. trans- Golgi | iii. Cop I vesicle budding. |
| D. Cop II vesicles | iv. Mannose-6-phosphate receptor |
| E. Endocytic vesicles | v. Protein aggregate for secretion. |
Choose the option that matches the organelles with the most appropriate property.
A - iv; B - iii; C - v; D - i; E - ii
A - v; B - iv; C - i; D - v; E - ii
A - iii; B - v; C - i; D - iv; E - ii
A - iv; B - v; C - ii; D - i; E - iii
Cell cycle checkpoints are surveillance mechanisms that ensure order and fidelity of events of the cell cycle. Given below are some of the checkpoint proteins and their functions.
| A. Mad2 | i. Prevention of Cdc 14 activation. |
| B. Tem 1 | ii. Prevention of Cdc20 activation. |
| C. ATM, ATR | iii. Inhibition of p21CIP |
| iv. Inhibition of separase action |
Match the checkpoint protein with its function.
A - iv; B - i and ii C - iii
A - ii and iv; B - i; C - iii
A - ii; B - i and iii; C - iv
A - ii and iv; B - iii; C - i
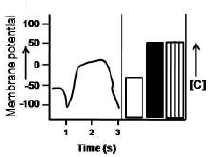
Fertilization in sea urchin involves interaction of sperm Bindin with its receptor EBR1, a 350 kDa glycoprotein on the egg vitelline membrane. The plot given below shows the status of membrane potential and levels of EBR1, Na+ and K+ in an unfertilized egg.

Which one of the following graphs best represents the condition within an egg 1-3 seconds after fertilization?



Several types of molecules including the transmembrane glycoproteins can function as matrix receptors and co-receptors. However, the principal receptors on animal cells for binding most extracellular matrix proteins are the integrins. Which of the following statements is NOT true for integrins?
Integrins are transmembrane linker proteins that link to the cytoskeleton.
An integrin molecule is composed of two non-covalently associated glycoprotein subunits α and β. Both subunits span the cell membrane, with short intracellular C-terminal tails and large N-terminal extracellular domains.
the extracellular portion of the integrin dimer binds to specific carbohydrate residues in extracellular matrix proteins.
The intracellular portion binds to a complex of proteins that form a linkage to the cytoskeleton.
Which one of the following statements related to components/features of senescence in plants is INCORRECT?
Programmed cell death in plants may generate functional cells or tissues.
Senescence can be induced by application of cytokinins and delayed by overexpression of salicylic acid
Plants defective in autophagy demonstrate accelerated plant senescence
Leaf senescence is regulated by NAC and WRKY genes families.
Prestin, a membrane protein, is found in which one of the following cells of the organ of Corti?
Inner hair cells
Inner phalangeal cells
Outer hair cells
Outer phalangeal cells
Which one of the listed below is a P-type ion transporter?
Mg2+ and fe2+
Mg2+ and fe3+
Mg2+ and Cl-
Na+, -K+, Ca2+ and H+
D.
Na+, -K+, Ca2+ and H+
P-type ion transporter forms a phosphorylated (P-) intermediate state during their ion transport cycle. Members of this family generate and maintain crucial (electro-) chemical gradients across cellular membranes, by translocating cations, heavy metals and lipids. The ions bind to the transmembrane domain, coordinated by negatively charged and polar residues, in a region between transmembrane helices M4, M5, M6 and M8. The number of transported ions varies: the fungal H+ -ATPase transports one H+, SERCA transports two Ca2+ out versus two to three H+ in, and the NKA transports three Na+ out and two K+ in
Match the enzymes is Column A with their respective biological functions in column B:
| Column A | Column B |
| (a) Lipases | (i) Catalysis of ATP-dependent translocation of the aminopholipids, phosphatidylethamine and phosphatidy-lserine from the plasma membrane |
| (b) Flippases | (ii) Catalysis of ATP-dependent translocation of plasma membrane phospholipids from the cytosolic to the extracellular leaflet. |
| (c) Floppases | (iii) Catalyze hydrolysis of triacylgycerols. |
| (d) Scramblases | (iv) Catalyze the movement of any membrane phospholipid across the bilayer down its concentration gradient. |
Choose the correct combination of answers from the given options given below:
| (a) | (b) | (c) | (d) | |
| A | (iii) | (i) | (ii) | (iv) |
| (a) | (b) | (c) | (d) | |
| B | (i) | (iii) | (iv) | (ii) |
| (a) | (b) | (c) | (d) | |
| C | (iv) | (ii) | (i) | (iii) |
| (a) | (b) | (c) | (d) | |
| D | (ii) | (iv) | (iii) | (i) |
