 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsFlowers represent a complex array of functionally specialized structures that differ substantially from the vegetative plant body in form and cell types. Following are statements made regarding floral meristems.
A. Floral meristems can usually be distinguished from vegetative meristems by their larger size.
B. The increase in the size of the meristem is largely a result of increased rate of cell division in central cells.
C. The increase in the size of the meristem is due to larger size of the cells, which in turn results from rapid cell expansion only.
D. A network of genes control floral morphogenesis in plants.
Which combination of the above statements is true?
A, B and D
A, B and C
B, C and D
A, C and D
Three embryos, X (wild type), Y (mutant for bicoid) and Z (mutant for nanos) were injected with bicoid mRNA in their posterior pole at early cleavage stage. What would be the phenotypes of the resulting embryos?
Embryo X will develop head on both anterior and posterior side, while embryos Y and Z will develop head on posterior side only.
Embryos X and Z will develop head on both anterior and posterior side, while embryo Y will develop head on posterior end only.
Embryos X, Y and Z will develop head on both anterior as well as posterior side.
Embryo X will develop head on anterior side, embryo Y will develop no head, while embryo Z will develop head on anterior as well posterior side.
In C.elegans during embryogenesis, an anchor cell and 6 hypodermal vulval precursor cells (VPCs) get involved in forming the vulva. If 3 of the hypodermal VPCs are killed by a laser beam, a normal vulva is still formed. This could be due to the following possible reasons.
A. Six hypodermal VPCs form equivalence group of cells, out of which only 3 participate in vulva formation and 3 cells remain as reserve cells.
B. When 3 hypodermal VPCs are killed, the neighboring hypodermal non-VPCs get freshly recruited.
C. Anchor cell functions as an inducer which can induce epithelial cells of the gonad to get recruited to compensate for the loss.
D. Anchor cell functions as an inducer which can induce epithelial cells of the gonad to recruited to compensate for the loss.
E. Anchor cell acts as an inducer which can spatially induce only 3 hypodermal cells to form the vulva.
Which combination of the above statements is correct?
A and B
B and C
C and D
A and D
In tadpoles, if the tail is amputated it can regenerate. However, if the tail is amputated and then exposed to retinoic acid, it develops limbs instead of regenerating the tail. This could be due to the following reasons:
A.Retinoic acid is a morphogen and induces genes responsible for limb formation.
A. Retinoic acid raises the positional value in that region for limb development to take place.
B. This is a random phenomenon and is not well understood.
C. Retinoic acid possibly acts as a mutagen and the phenotype observed is a result of several mutations.
Which combination of the above statements is true?
A and B
C and D
B and D
B and C
In sea urchins, a group of cells at the vegetal pole become specified as the large micromere cells. These cells are determined to become skeletogenic mesenchyme cells that will leave the blastula epithelium to ingress into the blastocoel. The specification is controlled by the expression of Pmar 1 which is a repressor of HesC. HesC represses the genes encoding transcription factors activating skeleton forming genes. The gene regulatory network is given below:
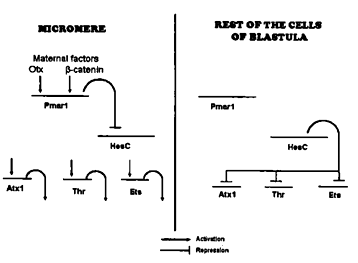
Below, column I lists the experiments carried with mRNA/ antisense RNA of different genes injected into single celled sea urchin embryo while Column II lists the developmental outcomes:
Match the following:
|
Column I (Injection of) |
Column II (developmental outcomes) |
| A. mRNA of Pmar 1 | 1. All cells will start ingressing into blastocoel. |
| B. mRNA od HesC | 2. Skeletonmesenchyma will not be found |
| C. Antisense of Pmar1 | |
| D. Antisense of HesC |
Which of the following combinations is correct?
A – 2; B- 1; C – 1; D – 2
A – 1; B – 1; C – 2; D – 2
A – 1; B – 2; C – 2; D – 1
A – 2; B – 2; C – 2; D - 2
Identify the pollinators for the flowers with following pollination syndromes
A. Flowers dull coloured, located away from foliage, floral parts turgid.
B. Flowers bright red, crowded, turgid, nectar watery and sucrose rich.
C. Flowers white with pleasant odor, corolla tube long, night blooming.
(A) Bird; (B) Bat; (C) Butterfly
(A) Bat; (B) Bird; (C) Moth
(A) Bat; (B) Bird; (C) Bee
(A) Bird; (B) Bat; (C) Carrion fly
During apoptosis, phosphatidyl serine (PS) usually present in the inner leaflet of the plasma membrane flips to the outer membrane. Annexin V is a protein that binds to PS. Using this as a tool, we identify the apoptotic cells from necrotic and normal cell populations by FACS using FITC-tagged Annexin V. Propidium iodide (PI) is used to stain the nucleus which generally identifies necrotic and late apoptotic cells. In which area of the plot you should get early apoptotic cells by FACS analysis?
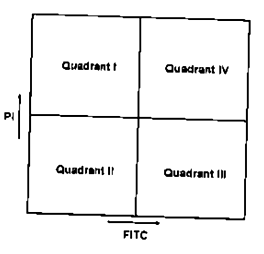
Quadrant I
Quadrant II
Quadrant III
Quadrant IV
The following table shows survival and fertility data for a seasonally breeding species
| SEASON | PROPORTION SURVIVING | FERTILITY |
| 0 | 1.0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0.5 | 20 |
| 2 | 0.0 | - |
Based on above data, net productive rate (R0) of the species will be
1
5
10
20
A cross was between pure wild type males and brown eyed, curled winged females of D. melanogaster. The F1 females were test crossed. The F2 progeny obtained was as follows:
Wild type 200
Brown eyes, curled wings 150
Brown eyes, normal wings 30
Normal eyes, curled wings 20
Total 400
The genetic distance (cM) between brown eye and curled wing loci is:
12.5
50
150
25
The ced-9 gene appears to be a binary switch that regulates cellular survival and apoptosis in nematodes. Considering that CED-9 protein can bind to and inactivate CED-4, which of the following would lead to apoptosis?
Activation of ced-9 gene
Loss of function of CED-3
Loss of function of ced-9 gene
Loss of function of CED-4
