 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsMouse bone marrow cells were fractionated to derive stem cells antigen‐1+ (Sca‐1+) cells. These cells were cultured with interleukin‐3 or granulocyte‐macrophage colony stimulating factor, or macrophage‐colony stimulating factor, or granulocyte colony stimulating factor. Most numerous and varied colonies were obtained in the culture stimulated with
Interleukin-3
Granulocyte‐macrophage colony stimulating factor
Macrophage‐colony stimulating factor
Granulocyte‐colony stimulating factor
Cancer causing genes can be functionally classified into mainly three types (a) genes that induce cellular proliferation, (b). tumor suppressor genes, (c) genes that regulate apoptotic pathway. Epstein‐Barr virus that cause cancer by modulating apoptotic pathway, contain a gene having sequence homology with which of the following genes?
bax
bcl-2
p53
caspase-3
Toll like receptor 4 is associated with responsiveness to LPS, an endotoxin that causes lethal endo‐toxic shock. The mice deficient in Toll like receptor 4 and BALB/c mice were injected with Escherichia coli. In addition, some BALB/b mice were also injected with the same bacteria alone or with anti‐interleukin‐10 (IL‐10) antibody. The mice resistant to the lethal effect of bacteria were
BALB/b mice receiving the bacteria
BABL/b mice receiving the bacteria and the anti IL‐10 antibody
Mice deficient in Toll like receptor
BALB /c mice receiving the bacteria
Macrophages were collected from BALB/c mice, CD40 deficient mice, CD86 deficient mice and ICAM‐1 deficient mice. These macrophages were co‐cultured with LCMV peptide specific T cells in presence of the LCMV peptide for three days. The cells were recovered and co‐cultured with BALB/c derived macrophages in presence of the peptide. During the last twelve hour of the co‐culture, 3H thymidine was added to the cultures. The cells were harvested and 3H thymidine incorporation was assessed. The highest incorporation was observed in
BALB/c macrophage‐T cell co‐culture
CD40 deficient macrophage‐T cell co-culture
CD86 deficient macrophage T cell co‐culture
ICAM‐1 deficient macrophage T cell co culture
During early cleavage of Caenorabditis elegans embryos, each asymmetrical division produces one founder cell which produces differentiated descendants and one stem cell. The very first cell division produces one anterior founder cell, namely AB and one posterior stem cell, namely P1. When these blastomers are experimentally separated and allowed to proceed further with development, one could get the following possible outcomes:
P1 cells would develop autonomously while the AB would show conditional development
P1 cells would show conditional development while AB would show autonomous development
Both would show autonomous specification and results in mosaic development
Both would show conditional specification and results in regulative development
A.
P1 cells would develop autonomously while the AB would show conditional development
C.elegan has isolecithal yolk distrubion. The zygote of Caenorhabditis show rotational holoblastic cleavage. The first cell division takes place asymmetically along the anterior-posterior axis of the egg. Founder cell(AB) and stem cell (P1) get produce as the product of the first cleavage.
In case of sea urchin, which of the following is the correct sequence of events taking place during the interaction of sperm and egg?
Chemo‐attraction of sperm to the egg by soluble molecules secreted by the egg → exocytosis of the sperm acrosomal vesicles to release its enzymes → binding of the sperm to the extracellular matrix of the egg →passage of sperm through this extracellular matrix → fusion of egg and sperm cell membranes
Chemo‐attraction of sperm to the egg by soluble molecules secreted by the egg → binding of the sperm to the extracellular matrix of the egg → exocytosis of the sperm acrosomal vesicle to release its enzymes → passage of sperm through this extracellular matrix → fusion of egg and sperm cell membranes.
Chemo-attraction of sperm to the egg by soluble molecules secreted by the egg → binding of the sperm to the extracellular matrix of the egg → exocytosis of the sperm acrosomal vesicles to release its enzymes → fusion of egg and sperm cell membranes.
Chemo-attraction of sperm to the egg by soluble molecules secreted by the egg → passage of sperm through this extracellular matrix → binding of the sperm to the extracellular matrix of the egg → exocytosis of the sperm acrosomal vesicle to release its enzymes → fusion of egg and sperm cell membranes.
Injection of noggin mRNA into a 1‐cell, UV‐irradiated embryos of frog completely rescues dorsal development and allows the formation of complete embryo. Some of the following statements (A‐D) could possibly explain this observation:
A. Noggin is a secreted protein which induces dorsal ectoderm to form neural tissue and it dorsalizes the mesoderm cells which would otherwise contribute to ventral mesoderm.
B. Noggin binds directly BMP4 and BMP2 thus preventing complex formation with their receptors.
C. Noggin along with other molecules prevent BMP from binding to and inducing ectoderm and mesoderm cells near the organizer.
D. Noggin is a secreted protein which induces the dorsal ectoderm to form the epidermis and it ventralize the mesoderm cells which would otherwise contribute to dorsal mesoderm.
Which of the above statements are correct?
A,B and C
A and B
B and C
A and C
In a stressful condition, ACTH secretion was increased and as a result glucocorticoid concentration was elevated in blood. One or a combination of the following changes most likely taking place in this condition:
A. Decreased circulating eosinophills and basophils
B. Reduced IL2 release
C. Potentiated inflammatory response to tissue injury
D. Increased mitotic activity of lymphocytes in lymph nodes
The correct options are:
B and C
A and B
B and D
C and D
Which of the following graph represents normal sexual cycle in a normal human female? ( ---- this line represent progestrone and — this one for estrogen. X-axis =Femal sexual cycle (days), Y-axis= Concentration)

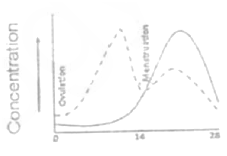
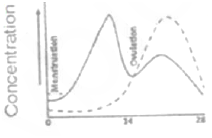
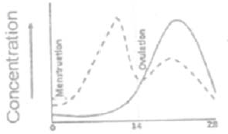
Which of the following maternal effect gene products regulate production of anterior structures in Drosophilia embryo?
Bicoid and Nanos
Bicoid and Hunchback
Bicoid and Caudal
Nanos and Caudal
