 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsAntennapedia complex in Drosophila contain five genes, lab, pb, dfd, scr, and Antp and they express in parasegments 1to 5, respectively in a non-overlapping manner. In the larva or in later stages of development, the region of Antp (Antennapedia) expression corresponds to a part of second thoracic segment. A mutation in Antp is known to cause transformation of antenna to leg-like structures.
Below are certain statements made in respect to the functions of Antennapedia:
A. In the above described Antp mutation, the gene ectopically expresses in the head region.
B. One of the functions of Antp is to repress genes that induce antenna development.
C. Anto expresses in thorax and forms a concentration gradient in the posterioanterior direction, thus affecting head development.
D. A homozygous recessive mutation of Antp is expected to transform the leg to antenna in the second thoracic segment.
Which combination of the above statements correctly describes the function of Antennapedia?
A, B, and C
B and C
C and D
A, B, and D
D.
A, B, and D
Among the given statements, the correct set of statements are A, B, and D.
Match the following cleavage patterns with the species in which they occur.
| Species | Cleavage pattern |
| A. Flatworm | i. Meroblastic discoidal |
| B. Frog | ii. Meroblastic superficial |
| C. Birds | iii. Holoblastic displaced radial |
| D. Insect | iv. Holoblastic spiral |
A - iv; B - iii; C - i; D - ii
A - iii; B - i; C - iv; D - ii
A - ii; B - iii; C - i; D - iv
A - ii; B - iv; C - iii; D - i
Which one of the following statements regarding limb development in mice is true?
The gene encoding Tb×5 is transcribed in the limb fields of the hindlimbs.
The gene encoding Tb×4 is transcribed in the limb fields of the forelimbs.
Genes encoding Islet 1, Tb×4 and Pitx are expressed in the presumptive hindlimb.
Genes encoding Islet 1, Tb×4 and Pitx are expressed in the presumptive forelimb.
Based on ABC model during flower development, loss of class A activity results in the formation of only stamen and carpel. Which of the following floral organ identity genes controls the class A activity?
APETALA 1 and APETALA 2
APETALA 3 and PISTILLATA
Only PISTILLATA
Only AGAMOUS
In a given experiment, transplantation of micromeres from the vegetal pole of a 16-cell sea urchin embryo onto the animal pole of a host 16-cell sea urchin embryo would initiate:
the transplanted micromeres to invaginate into the blastocoel to create a new set of skeletogenic mesenchymal cells.
the transplanted micromeres to ingress into that blastocoel to create a new set of skeletogenic mesenchymal cells.
the transplanted micromeres will mingle with the host micromeres to ingress into the blastocoel to create skeletogenic mesenchyme cells.
the transplanted micromeres will form the secondary archenteron.
Orchids of the genus Cryptostylis are known to maintain reproductive isolation because their flowers look and smell like females of the wasps of genus Lissopimpla. When the male wasp visits and attempts to mate with the flower, the shape of anther and stigma allows correct placement and transfer of pollen to the wasp, which then transfers the pollen to species-specific flower that it net attempts to mate with. This prezygotic barrier that prevents inter-species cross-pollination in Cryptostylis is best explained by:
behavioural isolation through mimicry.
mechanical isolation through mimicry
temporal isolation
habitat isolation
A 20-week old infant was exposed to the following stimuli and the responses were measured.
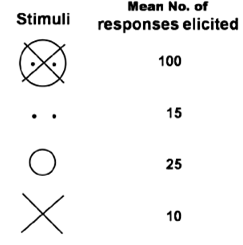
Based on the response patterns shown above to the given stimuli, select the correct theory that best describes the observed responses.
Heterogenus summation
Gestalt priniciple
Supernormal stimuli
Sign stimulus
A gene 'X' in Drosophila contributes to the inviability of hybrids. The phylogeny below shows the evolutionary history of gene 'X' and on each branch the numbers indicate the non-synonymous/ synonymous substitutions.
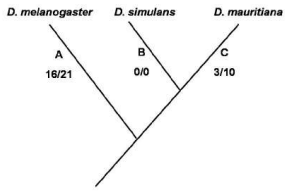
Based on the above information, select the correct statement from the choices below:
High proportion of non-synonymous changes at A indicates evolution by natural selection.
High proportion of synonymous changes at A indicates absence of natural selection.
Equal proportion of non-synonymous and synonymous changes at B indicates deleterious selection.
Low proportion of non-synonymous changes at C indicates positive selection.
Match the two columns that represent plant organs (I) and parts within these organs (II).
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Carpel | i. Petals, corolla |
| B. Perianth | ii. Vegetative cell, generative cell |
| C. Microsporocyte | iii. Stigma, style, ovary |
| D. Megasporocyte | iv. Antipodal cells, polar nuclei, synergid cells |
A - i; B - iii; C - ii; D - iv
A - iii; B - iv; C - i; D - ii
A - i; B - iii; C - iv; D - ii
A - iii; B - i; C - ii; D - iv
Given below are statements on key characteristics of two fungal lineages.
(A) Microsporidia do not have true mitochondria.
(B) Most chytridsproduce flagellated gametes.
(C) Microsporidia are usually free-living.
(D) Chytrids reproduce sexually without a dikaryon stage.
Choose the combination with correct statements.
A, B, and C only
A, B, and D only
B, C, and D only
A and B only
