 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsWhich one of the following is a type of intercellular junction in animal cells?
Middle lamella
Plasmodesmata
Desmosomes
Glycocalyx
Which of the following is a correct hierarchical sequence for classifying a living organism?
Domain - Kingdom - Phylum - Class - Order - Family - Genus - Species.
Kingdom - Domain - Phylum - Class - Order - Family - Genus - Species
Domain - Kingdom - Phylum - Order - Class - Family - Genus - Species
Kingdom - Domain - Phylum - Order - Class - Family - Genus - Species
B.
Kingdom - Domain - Phylum - Class - Order - Family - Genus - Species
The correct hierarchical sequence for classifying a living organism is - Kingdom - Domain - Phylum - Class - Order - Family - Genus - Species.
Branchiostoma is a
deuterostome and schizocoelomate
protostome and schizocoelomate
deuterostome and enterocoelomate
protostome and enterocoelomate
The organs 'radula' and clitellum' are found in
Coelenterata and Echinodermata, respectively
Echinodermata and Coelenterata, respectively
Annelida and Mollusca, respectively
Mollusca and Annelida, respectively
The following statements are related to excretion in invertebrates:
A. Flame cells are found in molluscs and jellyfish.
B. Nephridia and Malphigian tubules convert ammonia to urea for water conservation.
C. Green glands are found in flatworms and help in the excreta elimination.
D. Excretory canals in nematodes carry waste materials to excretory pores in the body wall.
Choose the correct answer.
Only C
A and C
Only B
B and D
The diagram below depicts a simplified Tree of Life with three domains and one of the domains including Whittaker's three major kingdoms.
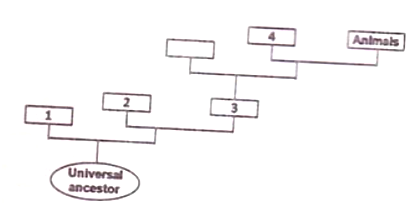
Which of the following is the correct naming of the numbered boxes?
1- Bacteria; 2 - Archaea; 3 - Eukarya; 4 - Fungi
1 - Archaea; 2 - Bacteria; 3 - Eukarya; 4 - Plants
1 - Eukarya; 2 - Bacteria; 3 - Archaea; 4 - Plants
1 - Archae; 2 - Bacteria; 3 - Eukarya; 4 - Fungi
Sleeping sickness is a disease caused by a protozoan parasite and the following statements pertain to that disease:
A. The vector for this disease is tsetse fly.
B. The vector for this disease is Trypanosoma brucei.
C. The parasite's body is covered by a dense coat of variable surface glycoprotein (VSG).
D. There are several thousands of VSG genes, only one of them expressing at a time, which helps the parasite in evading the 's immune response.
E. Several thousand copies of VSG genes express concurrently, paralyzing the host immune system.
Which of the following is the correct combination of the statements given above?
B, C, and D
A, C, and D
A, C, and E
B, C, and E
Fish species X and Y feed on mayfly nymphs in their stream habitat. In a laboratory experiment, the predation intensity of X and Y on their prey was tested under dark (D) and light (L) conditions. Thus, the experimental protocol included four aquaria - LX, LY, DX, and DY. In each aquarium containing 100 mayfly nymphs, one fish was introduced and allowed to feed for 30 minutes. Then the fish was removed and the number of mayfly nymphs left uneaten in each aquarium was counted. The results are shown graphically below
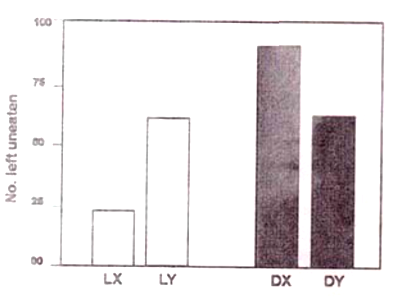
The most significant conclusion from the results is:
X is a visual predator, but has less predation impact on the prey than Y.
X is a visual predator and has greater predation impact on the prey than Y.
Y is a visual predator and has greater predation impact on the prey than X.
Y is a visual predator but has less predation impact on the prey than X.
Following are the characteristics of species that make them more or less prone to extinction:
| Rare - a | Common - b |
| Good dispersal rate - c | Poor dispersal rate - d |
| Low specialization - e | High specialization - f |
| High variability - g | Low variability - h |
| Low trophic status - i | High trophic status - j |
| Long life span - k | Short life span - l |
| High reproductive output - m | Low reproductive output - n |
Which of the following is the correct combination characteristics that makes the species more prone to extinction?
a d e f g j l n
a c f h i k m
b d e g i l n
b c f h j k m
Some key characteristics of the four classes of phylum Mollusca are listed below:
A. They have two lateral (left and right) shells (valves) hinged together dorsally; they do not have distinct head or radula; they disperse from place to place largely as larvae.
B. They generally creep on their foot; the heads of most of this group have a pair of tentacles with eyes at the end; during embryological development, they undergo torsion.
C. They have oval bodies with overlapping calcareous plates; underneath the plates, the body is not segmented; they creep along using a broad, flat foot surrounded by a groove or mantle cavity in which the gills are arranged.
D. They have a highly developed nervous system; most members of this class have closed circulatory systems.
The correct match of the above characteristics with the classes of Mollusca is
A - Polyplacophora; B - Bivalvia; C - Gastropoda; D - Cephalopoda
A - Cephalopoda; B - Polyplacophora; C - Bivalvia; D - Gastropoda
A - Bivalvia; B - Gastropoda; C - Polyplacophora; D - Cephalopoda
