 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsWhich of the following groups represents SAR clade of protists?
Euglenozoans, Red algae, Parabasilids
Brown algae, Forams, Radiolarians
Slime moulds, Entamoebas, Diplomonads
Charophyes, Choanoflagellates, Tubulinids
Following table shows a list of clades and plant:
| Clades | Plant |
| (a) Basal angiosperms | (i) Black pepper |
| (b) Magnolids | (ii) Orchid |
| (c) Monocots | (iii) Star anise |
| (d) Eudicots | (iv) Strawberry |
Which one of the following is correct match for the above?
| (a) | (b) | (c) | (d) |
| (iii) | (iv) | (ii) | (i) |
| (a) | (b) | (c) | (d) |
| (i) | (i) | (iii) | (iv |
| (a) | (b) | (c) | (d) |
| (ii) | (iv) | (iii) | (i) |
| (a) | (b) | (c) | (d) |
| (iii) | (i) | (ii) | (iv) |
The phylogenetics tree below shows evolutionary relationships among 8 species. Males of these species are either blue (b) or red (r) in color, the color being indicated next to each species name.
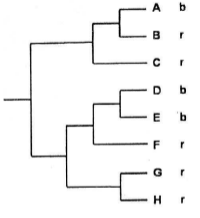
Based on the principle of parismony, which of the following statements best represents the evolution of male body color in this set or species?
The most recent common ancestor of all 8 species was blue; red evolved independently 5 times.
The most recent common ancestor of all 8 species was blue; red evolved independently 4 times.
The most recent common ancestor of all 8 species was red; blue evolved independently 3 times.
The most recent common ancestor of all 8 species was red; blue evolved independently 2 times.
A list of floral formulae and plant families are given in the following table:
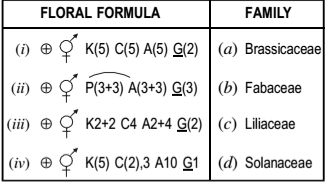
Which of the following option most appropriately matches given plant families with their representative floral formulae?
(i)-d, (ii)-(b), (iii)-(a), (iv)-(c)
(i)-(d), (ii)-(c), (iii)-(a), (iv)-(b)
(i)-(d), (ii)-(c), (iii)-(b), (iv)-(a)
(i)-(a), (ii)-(c), (iii)-(b), (iv)-(d)
Which of the following plastid coding region(s) have been recommended as a core barcode by Plant Working Group of the consortium for the Barcode of Life?
CO1 and rbcL
rbcL and matK
CO1 and matK
rbcL only
B.
rbcL and matK
Based on assesments of recoverability, sequence quality, and levels of species discrimination, a core two-locus combination of rbcL and matK as the plant barcode was recommended. This combination was shown to successfully discriminate among 907 samples from 550 species at the species level with a probability of 72%. The group admits that the two-locus barcode is far away from perfection due to the limited identification rate, and thus further research for other appropriate candidates is necessary. Additional combinations of noncoding and coding plastid regions have been tested for barcoding purpose
