 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsThe population size of a bird increased from 600 to 645 in one year. If the per capita birth rate of this population is 0.125, what is its per capita death rate?
0.25
0.15
0.05
0.02
The present global warming trend is expected to result in an increased incidence of malaria in temperate countries. the supposed underlying mechanism is that
higher temperatures make temperate country people more vulnerable to diseases.
malarial parasite grows better at higher temperatures.
the vector mosquito species require warmer temperatures for reproduction.
anti-malaria drugs are less effective in temperate countries.
The most important reproductive strategies of big trees in a forest are
earlier age at first reproduction and production of a larger number of small seeds.
earlier age at first reproduction and production of a small number of large seeds.
later age at first reproduction and production of a large number of small seeds
later age at first reproduction and production of a small number of large seeds.
In a very small population, genetic variation is often lost through genetic drift. If the population size of a mammal on an isolated island is 50, what percentage of its genetic variation is lost every generation?
0.01
0.5
0.1
0.05
There are three species of frogs - A, B and C. Species A does not provide parental care for its eggs and larvae. Species B is subjected to predation by a predator that selectively feeds only on small-sized larvae. Species C faces progressively decreasing opportunities for breeding with increasing age. Assuming that resources available for reproduction are similar for A, B, and C, which of the following strategies would have been favored?
A should produce a large number of small-sized offspring; B should produce a small number of large-sized offspring; C should breed earlier in life.
Species A and B should produce a small number of large-sized offspring and C should breed earlier in life.
Both species A and B should produce a large number of small-sized offspring and C should breed later in life but increase its clutch size.
Species A should produce a small number of large-sized offspring; B should produce a large number of small-sized offspring and C should breed earlier in life with a small clutch size.
The three graphs (A, B, C) show population growth (N) patterns in relation to N or time (t).
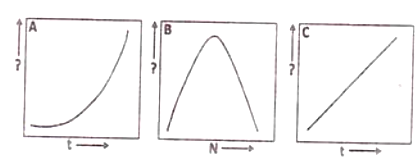
Which of the following is correct with reference to the Y-axis label and the type of population growth?
A : Y-axis: N, exponential growth; B : Y-axis: dN/dt, logistic growth; C : Y-axis: ln(N), exponential growth
A: Y-axis: dN/dt, exponential growth; B: Y-axis: ln(N), logistic growth; C: Y-axis: N, exponential growth
A: Y-axis: ln(N), exponential growth; B: Y-axis: dN/dt, logistic growth; C: Y-axis: N, exponential growth
A: Y-axis: dN/dt, exponential growth; B: Y-axis : ln(N), logistic growth; C: Y-axis: N, exponential growth
Which of the following set of observations is true with reference to a comparison of aquatic (A) and terrestrial (T) ecosystems?
Number of trophic levels is more in A than in T.
Productivity/ Biomass ratio is higher in T than in A.
Herbivore assimilation efficiency is higher in A than in T.
Number of trophic levels is more in T than in A.
Productivity/ Biomass ratio is greater in A than in T.
Herbivore assimilation efficiency is higher in A than in T.
Number of trophic levels is more in T than in A.
Productivity/ Biomass ratio is higher in T than in A.
Herbivore assimilation efficiency is higher in T than in A.
Number of trophic levels is more in A than in T.
Productivity/ Biomass ratio is greater in A than in T.
Herbivore assimilation efficiency is higher in A than in T.
A small lake has three trophic levels- phytoplankton (autorophs), Zooplankton (herbivore) and planktivorous fish (primary carnivore). Into this lake, a population ofpiscivorous fish (secondary carnivore) was introduced to study the 'top-down' effects. What is the expected long-term consequence of such an introduction to phytoplankton and zooplankton trophic levels?
Zooplankton biomass will increase and phytoplankton biomass will decrease.
Zooplankton biomass will decrease and phytoplankton biomass will increase.
The biomasses of both zooplankton and phytoplankton will increase.
The biomasses of both zooplankton and phytoplankton will decrease.
Following is the diagram of three idealized survivorship curves of animals:
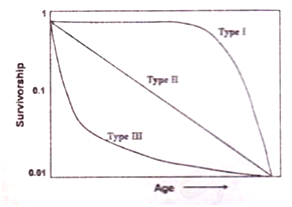
Find the correct match between the group of animals and the respective survivorship curves.
Marine pelagic fish and large mammals-III and I, respectively
Marine pelagic fish and large mammals-I and II, respectively.
Some birds and large mammals-I and III respectively.
Marine pelagic fish and some birds-I and III, respectively.
Four different species concepts are given below:
A. Species separate based on their use of different ecological niches and their presence in different habitats and environments.
B. Differences in physical characteristics or molecular characteristics are used to distinguish species.
C. Species are distinct if they are reproductively isolated.
D. Phylogentic trees and analyses of ancestry serve to differentiate species.
Which of the following gives the correct names of the above concepts?
A - Biological; B - Phylogenetic; C - Evolutionary; D - Ecological
A - Ecological; B - Phylogenetic; C - Biological; D - Evolutionary
A - Evolutionary; B - Ecological; C - Biological; D - Phylogentic
A - Phylogenetic; B - Evolutionary; C - Ecological; D - Biological
