 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsWhich one of the following statements is TRUE for positive-frequency dependent selection?
Fitness of a genotype increases as it becomes less common.
Fitness of a genotype increases as it becomes more common.
Fitness of a genotype decreases as it becomes less common
Fitness of a genotype decreases as it becomes common and gets fixed.
An integral membrane protein (P) has been identified as a cell surface protein of hepatocytes and assigned to bind to hepatitis B virus (HBV) and promote its entry into cytosol. Upon binding to HBV particles, the C-terminal of P interacts with F-actin in the cytosol and in turn, helps in the entry of the HBV particles. P was successfully cloned and expressed in animal cells in culture wherein its N-terminal is exposed on the surface while the C-terminal resides in the cytosol. The recombinant protein P so expressed retains its complete structure and function. From the list of experiments given below, which one of the experiments will you perform to show that C-terminal of the protein P via interacting with F-actin helps in HBV entry?
Incubating radiolabelled HBV with hepatocytes in culture and follow up its association with F-actin by immunoprecipitation analysis using anti-F-actin antibody.
Incubating radiolabelled HBV with hepatocytes over-expressing the C-terminal mutant of P and repeat the rest of the experiment as in “1”.
Incubating radiolabelled HBV with hepatocytes over-expressing the N-terminal mutant of P and repeat the rest of the experiment as in “1”.
Using wild type P as well as C-terminal mutant of P and their individual overexpression in a heterologous cell line (completely devoid of endogenous P protein) and then repeat experiment as in “1”.
Genes translocated to the heterochromatic regions of chromosomes are silenced. In S. pombe, a translocation event was detected wherein a gene of interest was translocated to the centromere region and is silenced. Mutagenesis leading to loss of function of the following target genes was done to allow expression of the gene of interest from its new locus.
(a) Mutation in histone deacetylase (Clr3).
(b) Mutation in histone acetyltransferase (HAT-8).
(c) Mutation in histone H3 lysine 9 methyl transferase (Clr4).
(d) Loss of Dicer, an RNA processing enzyme.
Which of the above events could allow the expression of this gene from the centromeric region?
(a), (b) and (c)
(a), (c) and (d)
(b) and (c) only D
(a) and (c) only
During maturation process of some RNA molecules, formation of a 2' – 5' phosphodiester bond takes place. Following statements are made about this phenomenon.
(a) Spliceosome mediated removal of intronic sequences occurs through the formation of a 2' – 5' phosphodiester bond.
(b) Removal of group II introns occurs through the formation of 2' – 5' phosphodiester bond.
(c) Enzymatic removal of introns from the yeast tRNA precursors involves 2' – 5' phosphodiester bond formation.
(d) RNaseP mediated 5'-end maturation of tRNA precursors involves formation of a 2' – 5' phosphodiester bond.
Which one of the following combinations of the statements is a true representation?
(a) only
(a) and (d)
(a) and (b)
(c) and (d)
A certain protein has been assumed to play an indispensable role in the survival of an intracellular parasite inside the host cells. Which one of the following techniques will best prove the assumption to be correct?
Treat the parasite-infected host cells with an inhibitor of the protein and check the number of parasites per host cell under the microscope.
Check the expression of the protein in parasite-infected host cells.
Check the activity of the protein in parasiteinfected host cells.
Treat the parasite-infected host cells with an activator of the protein and check the number of parasites per host cell under the microscope.
Two near inbred parental lines P1 and P2 of an angiosperm species are crossed to produce F1 seeds in which, the ploidy of the endosperm is 6N. If plants generated from these F1 seeds are backcrossed with P1, what will be the ploidy of the somatic cells in the next generation?
2N
4N
5N
6N
A virgin Drosophila female was crossed with a wild type male. The F1 progeny obtained had four types of males as shown below.
| Phenotype | White eyed | wild type | Cross vein less | White eyed and crossveinless |
| Number | 50 | 3 | 44 | 3 |
Assuming that white eye and crossveinless mutations are X-linked and recessive, the following statements were made:
(a) F1 females were also of four types as that of males.
(b) The white eyed crossveinless male flies appeared due to independent assortment.
(c) The map distance between the genes for white eye and crossveinless is estimated to be 12 cM.
(d) The map distance between white eye and crossveinless is estimated to be 6 cM.
(e) All F1 females are expected to be wild type.
(f) The F1 wild type males appeared due to crossing over.
The combination with correct statements is:
(c), (e), (f)
(a), (b), (d)
(a), (d), (f)
(b), (d), (e)
The locations of five overlapping deletions have been mapped to a Drosophila chromosome as shown below (Horizontal lines in the above figure indicate the deleted regions)
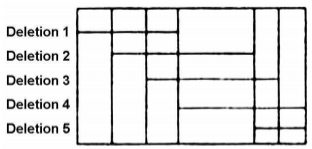
Recessive mutations a, b, c, d and e are known to be located within this region, but the order of mutations on the chromosome is not known. When the flies homozygous for the recessive mutations are crossed with flies homozygous for the deletions, the following results are obtained (letter “m” represents mutant phenotype and “+’’ represents the wild type).
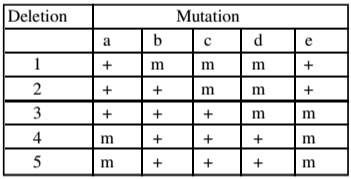
On the basis of the above data, the relative order of the five mutant genes on the chromosome is
b c d e a
a b c d e
b c e a d
c d b e a
The pedigree given below follows the inheritance pattern of a late-onset (after age of 30 years) genetic disease that is 100% penetrant. Affected individuals are indicated by a solid circle (woman) or solid square (males). RFLP analysis of DNA from each individual is shown below in the pedigree. Which grandchildren (IIIb to IIId) will be affected by the disease after attaining the age of 30 years?
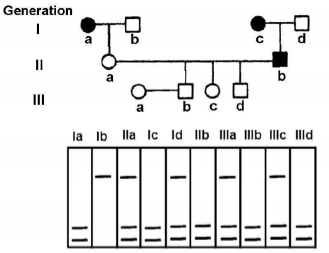
Only IIIb
Both IIIb and IIIc
Both IIIc and IIId
Both IIIb and IIId
A chemist synthesizes three new chemical compounds in the laboratory and names them as X, Y and Z. After analysing mutagenic potential of all these compounds, the geneticist observed that all are highly mutagenic. The geneticist also tested the potential of mutations induced by these compounds to be reversed by other known mutagens and obtained the following results
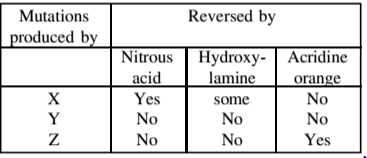
Assuming that X, Y And Z caused any of the three types of mutations, transition, transversion or single base deletion, what conclusions can you make about the nature of mutations produced by these compounds?
X causes transversion; Y causes transition; Z causes single base deletion
X causes transition; Y causes transversion; Z causes single base deletion
X causes transition; Y causes single base deletion; Z causes transversion
X causes transversion; Y causes single base deletion; Z causes transition
