 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsTwo pure lines of corn mean cob length of 9 and 3 inches, respectively. The polygenes involved in this trait exhibit additive gene action. Crossing these two lines is expected to produce a progeny population with mean cob length (in inches) of:
12.0
7.5
6.0
2.75
When two independent pure lines of pea with white flowers are crossed, the F1 progeny has purple flowers. The F2 progeny obtained from selfing shows both purple and white flowers in the ratio of 9:7. The following conclusions were made.
A. Two different genes are involved, mutations in which lead to the formation of white flowers.
B. These two genes show independent assortment.
C. This is an example of complementary gene action.
D. This is an example of duplicate genes.
Which of the above conclusion are correct?
A and C only
A and D only
A, B and D
A, B and C
Following are four modes of inheritance
(A) X-linked recessive
(B) X-linked dominant
(C) Autosomal recessive
(D) Autosomal dominant
Which of the above modes of inheritance and explain the pedigree shown below?
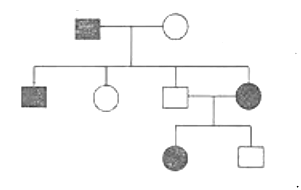
(A) and (C)
(B) and (C)
(C) and (D)
(D) only
C.
(C) and (D)
Inheritance that explains the above-given pedigree is Autosomal recessive and dominant.
Four different mutant lines showing similar phenotypes were identified from a genetic screen. When genetic crosses among these mutants were carried out, the first mutant was found to complement the second, third, and fourth mutant lines. However, no other complementation was observed. How many complementation groups do the four mutant lines belong to?
One
Two
Three
Four
There are ‘n’ number of alleles for a given locus in a diploid population. The proportion of all homozygotes in the population (i) if all alleles are equally abundant and (ii) if all alleles are not equally abundant, will be:
(i) 1/ n (ii) < 1/ n
(i) 1/ n (ii) > 1/ n
(i) 1/ n2 (ii) < 1/ n2
(i) 1/ n2 (ii) > 1/ n2
In hymenopteran insects, males are haploid and females are diploid. All fertilized eggs give rise to females and unfertilized eggs give rise to males. As a result, if a female mates with a single male, the females in the progeny are related to each other by 75%. But if the mother had mated with many males, the mean genetic relatedness of female progeny is correctly represented by:
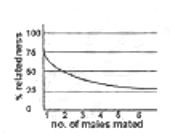
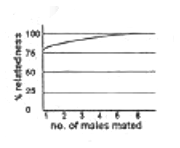

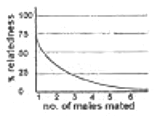
A chromosome aberration leads to change in the order of genes in a genetic map but does not alter its linkage group. This is due to
translocation
recombination
transposition
inversion
The concept of recon was proposed by Seymour Benzer by studying recombination between
lysis mutants of bacteriophage T4
white eye mutants of Drosophila melanogaster
biochemical mutants of Neurospora crassa
auxotrophic mutants of Escherichia coli
Aspartic acid (Asp) is specified by the codon GAU and GAC. After mutation, Asp is changed to Alanine represented by GCX, where X may be A, U, C, or G. The reversion of the mutation could only be done with reactive oxygen species. The nature of the mutation is considered to be
transition
transversion
either transition or transversion
depurination
A cross is made between two plants with white flowers. All the F1 progeny had red coloured flowers. This is because of
complementation
recombination
translocation
reversion
