 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsSomatic embryogenesis is an important exercise in micropropogation and genetic engineering of plants. The following steps are considered as critical for achieving somatic embryogenesis:
A. Reducing the concentration of sucrose in the medium by half.
B. Addition of the hormone, 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid, to induce somatic embryos.
C. Reduce agar concentration to 0.6% (w/v).
D. Use maltose in place of sucrose as a carbon source.
Which one of the following combinations is correct?
A and C
B and D
A and B
C and D
Of the following, which one of the individuals will NOT necessarily carry the allele responsible for the mentioned trait?
A woman in a family where an autosomal dominant trait is segregating and her mother and son are affected.
A daughter of a man who is affected by an X-linked dominant trait.
A father of a child who is affected with an autosomal recessive trait.
A father of a boy affected with X-linked recessive trait.
Three somatic hybrid cell lines, designated as X, Y and Z, have been scored for the presence or absence of chromosomes 1 through 8, as well as for their ability to produce the hypothetical gene product A, B, C, and D as shown in the following table:
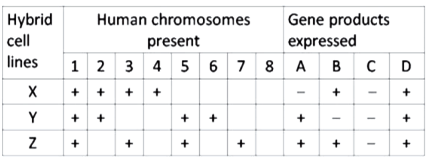
Which of the following option has most appropriately assigned chromosomes for each of the given genes?
Gene A on chromosome 5, Gene B on chromosome 3, Gene C on chromosome 8 and Gene D on chromosome 1.
Gene A on chromosome 5 and Gene B on chromosome 3 only.
Gene D on chromosome 8, Gene C on chromosome 1, Gene B on chromosome 5 and Gene A on chromosome 4.
Gene A on chromosome 5, gene B on chromosome 3, and Gene D on chromosome 1.
Consider the following hypothetical pathway:
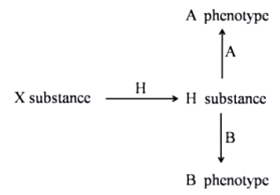
H allele converts X substance to H substance.
h allele cannot convert X to H substance and leads to phenotype 'O'.
A allele converts H substance leading to A phenotype.
a allele cannot convert H substance.
B allele converts H substance leading to B phenotype.
b allele cannot convert H substance.
An individual with A phenotype, when crossed with that of B phenotype, has a progeny with O phenotype. Which one of the following crosses can lead to the above observation?
Aahh × BbHH
AaHh × BBHh
AaHh × BBHH
AAHH × BbHh
Two siblings who inherit 50% of the genome from the mother and 50% from the father show lot of phenotypic differences. Which one of the following events during gametogenesis of the parents will maximally contribute to this difference?
Mutation
Recombination
Independent assortment
Environment
The following pedigree chart shows the inheritance of a given trait
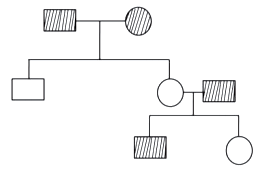
The trait can be called
autosomal dominant
autosomal recessive
X-linked dominant
sex limited
Mutation in a gene 'X' leads to lethality in a haploid organism. Which one of the following is best suited to analyze the function of gene 'X'?
Pleiotropic mutants
Temperature-sensitive mutants
Recessive mutants
Mutants with low temperature
Following is a hypothetical biochemical pathway responsible for pigmentation of leaves. The pathway is controlled b two independently assorting genes 'A' and 'B' encoding enzymes as shown below. Mutant alleles 'a' and 'b' code for non-functional proteins.
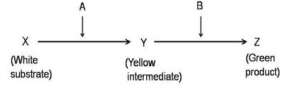
What is the expected progeny after selfing a plant with the genotype AaBb?
Green (9) : White (4) : Yellow (3)
Green (9) : Yellow (4) : White (3)
Green (9) : Yellow (6) : White (1)
Green (9): White (7)
A.
Green (9) : White (4) : Yellow (3)
The expected progeny after selfing a plant with genotype AaBb is Green (9) : White(4) : Yellow (3).
Consider an autosomal locus with two alleles A1 and A2 at frequencies of 0.6 and 0.4 respectively. Each generation, A1 mutates to A2 at a rate of μ = 1 × 10-5 while A2 mutates to A1 at a rate of 2 × 10-5. Assume that the population is infinitely large and no other evolutionary force is acting. The equilibrium frequency of allele A1 is
1.0
0.5
0.67
0.33
For two species A and B in competition, the carrying capacities and competition coefficients are-
KA = 150; KB = 200
α = 1.0; β = 1.3
According to the Lotka-Volterra model of interspecific competition, the outcome of the competition will be
Species A wins
Species B wins
Both species reach a stable equilibrium.
Both species reach an unstable equilibrium.
