 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsFive bacterial markers were followed for a co-transduction experiment. The following table documents the observations of this experiment. '+' denotes co-transduction and '-' denotes lack thereof; 'ND' stands for not determined.
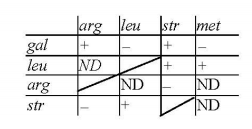
Pick the correct order in which the genes are arranged on the bacterial chromosome
str - gal - leu - arg - met
leu - met - arg - str - gal
leu - str - met - gal - arg
arg - gal - str - leu - met
A male mouse cell line has a large translocation from X chromosome into chromosome 1. When a GFP containing transgene is inserted in this chromosome 1 with translocation, it is often silenced. However, when inserted in the other homologue of chromosome 1 that does not contain the translocation, it is almost always expressed. Which of the following phenomenon best describes this effect?
Genome imprinting
Gene balance
Sex-specific expression
Dosage compensation
Two interacting genes (independently assorting) were involved in the same pathway. Absence of either gene's function leads to the absence of the end product of the pathway. A dihybrid cross involving the two genes is carried out. What fraction of the F2 progeny will show the presence of the end product?
1/4
3/4
9/16
15/16
A three-point test cross was carried out in Drosophila melanogaster involving three adjacent genes X, Y, and Z, arranged in the same order. The distance between X to Y is 32.5 map unit (mu) and that between X to Y is 20.5 map. The coefficient of coincidence = 0.886. What is the percentage of double recombinants in the progeny obtained from the testcross?
∼6%
∼8%
∼12%
∼16%
Fruit color of wild Solanum nigrum is controlled by two alleles of a gene (A and a). The frequency of A, p = 0.8 and a, q = 0.2. In a neighbouring field a tetraploid genotype of S. nigrum was found. After critical examination five distinct genotypes were found; which are AAAA, AAAa, AAaa, Aaaa and aaaa. Following Hardy Weingberg principle and assuming the same allele frequency as that of diploid population, the numbers of phenotypes calculated within a population of 1000 plants are close to one of the following:
AAAA : AAAa : AAaa : Aaaa : aaaa
409 : 409 : 154 : 26 : 2
420 : 420 : 140 : 18 : 2
409 : 49 : 144 : 36 : 2
409 : 420 : 144 : 25 : 2
Poplar is a dioecious plant. A wild plant with 3 genes AABBCC was crossed with a triple recessive mutant aabbcc. The F1 male hybrid (AaBbCc) was then backcrossed with the triple mutant and the phenotypes recorded are as follows:
| AaBbCc | 300 |
| aaBbCc | 100 |
| aaBbcc | 16 |
| AabbCc | 14 |
| AaBbcc | 65 |
| aabbCc | 75 |
| aabbcc | 310 |
| Aabbcc | 120 |
The distance in map unit (mu) between A to B and B to C is
25 and 17 mu, respectively
33 and 14 mu, respectively
25 and 14 mu, respectively
33 and 17 mu, respectively
Which one of the following statements is incorrect?
Loss of genetic variation occurs within a small population due to genetic drift.
The number of deleterious alleles present in the gene pool of a population is called the genetic load.
Genetic erosion is a reduction in levels of homozygosity.
Inbreeding depression results from increased homozygosity for deleterious alleles.
A mouse carrying two alleles of insulin-like growth factor II (IgF2) is normal in size; whereas a mouse that carries two mutant alleles lacking the growth factor is dwarf. The size of a heterozygous mouse carrying one normal and one mutant allele depends on the parental origin of the wild type allels. Such pattern of inheritance is known as
Sex-linked inheritance
Genomic imprinting
Gene-environment interaction
Cytoplasm inheritance
B.
Genomic imprinting
The pattern of inheritance is genomic imprinting.
Which one of the following statements is INCORRECT?
Quantitative inheritance results in a range of measurable phenotypic for a polygenic trait.
Polygenic traits often demonstrate continuous variation.
Certain alleles of quantitative trait loci (QTL) have an additive effect on the character/ trait.
Alleles governing quantitative traits do not segregate and assort independently.
Maternal inheritance of coiling of shell in snail (Limnaea peregra) is well established. The dextral coiling depends on dominant allele D and sinistral coiling depends upon recessive allele d. A female F1 progeny of dextral (Dd) type is crossed with a male sinistral snail. What will be the ratio of heterozygous: homozygous individuals in its F2 progeny?
3 : 1
1 : 1
1 : 3
1 : 2 :
