 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsWhich of the following is true for cells harbouring F'plasmid?
Their F plasmid is non-functional.
They exhibit increased rates of transfer of all chromosomal genes.
They are merodiploids.
They fail to survive as the chromosomal origin of replication is inactivated.
A pair of alleles govern seed size in a crop plant. 'B' allele responsible for bold seed is dominant over 'b' allele controlling small seed. An experiment was carried out to test if an identified dominant DNA marker (5kb band) is linked to alleles controlling seed size. A plant heterozygous for the marker and the alleles were crossed to a small-seeded plant lacking the 5Kb band. 100 progeny obtained from the cross were analyzed for the presence and absence of the DNA marker. The results are tabulated below:
| Phenotype |
Plant with bold seed
|
Plant with small seed
|
||||
| No. of progeny showing presence or absence of DNA marker |
|
|
Based on the above observations which one of the following conclusions is correct?
The DNA marker assorts independently of the phenotype.
The 5Kb band is linked to the allele 'B'.
The 5kb band is linked to the allele 'b'.
The DNA marker assorts independently with bold seed but is linked to the small trait.
The following scheme represents deletions (1-4) in the rII locus of phage T4 from a common reference point:

Four point mutations (a to d) are tested against four deletions for their ability (+) or inability (-) to give wild type (rII+) recombinants. he results are summarized below:
| a | b | c | d | |
| 1 | + | + | + | + |
| 2 | + | + | + | - |
| 3 | + | - | + | - |
| 4 | - | - | + | - |
Based on the above the predicted order of the point mutations is
b-d-a-c
d-b-a-c
d-b-c-a
c-d-a-b
The following pedigree shows the inheritance pattern of a trait.
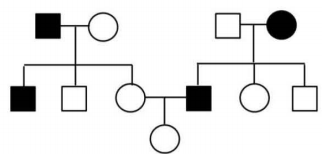
From the following select the possible mode of inheritance and the probability that the daughter in generation III will show the trait.
X-linked recessive, probability is 1/2.
X-linked recessive, probability is 1/4.
Autosomal recessive, probability is 1/2.
Autosomal recessive, probability is 1/3.
Interrupted mating experiments were performed using three different Hfr strains (1-3). The three strains have different combinations of selectable markers. The time of entry for markers for each strain is shown in the table below:
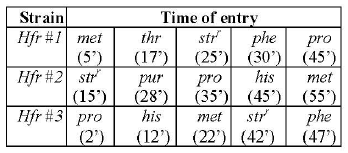
Using the above data, predict the correct sequence of markers on the E. coli chromosome.
met-thr-strr-phe-pro-purr-his
purr-pro-his-met-thr-strr-phe
strr-purr-his-met-phe-pro-strr
his-met-phe-thr-pro-strr-purr
A recessive inherited disease is expressed only in individuals of blood group O and not expressed in blood groups A, B or AB. Alleles controlling the disease and blood group are independently inherited. A normal husband with blood group B already had one child with the disease. The woman is pregnant for second time. What is the probability that the second child will also have the disease?
1/2
1/4
1/16
1/64
In a breeding experiment, two homozygous parental lines (P1 and P2) were crossed to produce F1 hybrids. Due to an experimental error, seeds of these hybrids got mixed up with the seeds of two other germplasm lines (P3 and P4) and hybrid seeds derived from them. A marker-based fingerprinting exercise was performed using six randomly selected seeds (F1-F6) from the mixed material and the mixed material and the four parental lines. Results of this analysis are shown below:
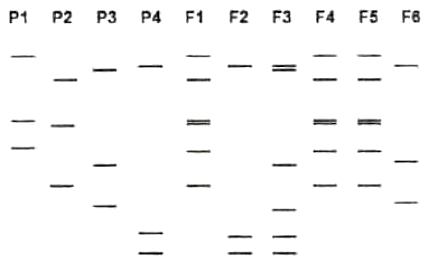
Based on the above data, which one of the following represents the correct set of parents and their F1 progeny?
P1 × P2 = F3
P3 × P4 = F2
P1 × P2 = F1
P3 × P4 = F6
In Tay-Sachs disease, accumulation of glycolipids occurs, especially in nerve cells. These cells are greatly enlarged with swollen lipid-filled endosomes and the children with this disease die at a very early stage. Such condition occurs due to specific defect in
specific lysosomal enzyme that catalyzes a step in the breakdown of gangliosides.
sorting of an enzyme that adds a phosphate group at 6th position of mannose in all acid hydrolases.
one of the Rab proteins involved in recycling of vesicles.
v-SNARE molecules which cause abnormal vesicle tethering and docking and affect vesicle fusion with lysosomes.
A.
specific lysosomal enzyme that catalyzes a step in the breakdown of gangliosides.
The condition occurs due to a specific lysosomal enzyme that catalyzes a step in the breakdown of gangliosides.
In a transduction experiment using a+b+c+ genotype as a donor and a-b-c- as the recipient, a+ transductants were selected and screened for b and c. The data obtained are shown below:
| Genotype | No. of recombinants |
| a+b-c- | 573 |
| a+b+c- | 98 |
| a+b-c+ | 11 |
| a+b+c+ | 68 |
The cotransduction frequencies for a+b+ and b+c+, respectively are
17% and 12%
22% and 9%
22% and 17%
17% and 9%
Two inbred lines of beans were intercrossed. In F1 the variance in bean length was measure as 2.0. The F1 was selfed to obtain F2 and the variance in bean length in F2 was 7.0. The broad heritability of bean length in the F2 population will be:
0.75
9.0
5.0
0.71
