 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsAn individual is having an inversion in heterozygous condition. The regions on normal chromosome are marked as A, B, C, D, E, F, G while the chromosome having inversion has the regions as a, b, e, d, c, f, g. The diagram given below shows pairing of these two homologous chromosomes during meiosis and the site of a crossing over is indicated:
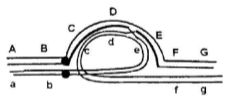
The following statements are given to describe the inversion and the consequence of crossing over shown in the above diagram:
(a) This is a pericentric inversion
(b) This will generate a dicentric and an acentric chromosome following separation of chromosomes after crossing over
(c) This will generate two monocentric recombinant chromosomes following separation of chromosomes after crossing over
(d) All the gametes thus formed will have deletion and/or duplication and will be nonviable
(e) 50% of the gametes having recombinant chromatid will be non-viable, while 50% gametes having non-recombinant chromatid will survive
(f) This is a paracentric inversion
Which combination of the above statements describe the inversion and meiotic consequences correctly?
(a), (b) and (c)
(a), (c) and (e)
(b), (e) and (f)
(c), (d) and (f)
D.
(c), (d) and (f)
The figure represents a paracentric inversion; centromere not involved in inversion. The characteristic dicentric (a chromatid with two centromeres) and acentric chromatid (having no centromere) is formed. During Anaphase when chromatids separate they result in deletion in recombinant gametes hence non viable whereas other two non recombinant gametes will be viable.
Following are key points about the effect of genetic drift:
(a) Genetic drift is significant in small populations.
(b) Genetic drift can cause allele frequencies to change in a predirected way.
(c) Genetic drift can lead to a loss of genetic variation within populations.
(d) Genetic drift can cause harmful alleles to become fixed.
Which one of the following combination of the above statements are true?
(a) and (b)
(a) and (c) only
(a), (b) and (c)
(a), (c) and (d)
Consider a single locus with 2 alleles which are at Hardy-weinberg equilbrium. If the frequency of one the homozygous genotypes is 0.64, what is the frequency of heterzygotes in the population?
0.16
0.20
0.32
0.36
Competitions for mates and variances in fitness is higher among females than among males in which of the following animals mating systems?
Monogamy
Polygyny
Polyandry
Sequential monogamy
Which one of the following will have the least impact on allele frequencies in small population?
Inbreeding
Random mating
Genetic drift
Outbreeding
In a genetic assay, randomly generated fragments of yeast DNA were cloned into a bacterial plasmid containing gene 'X' essential for yeast viability on minimal media. The recombinant plasmid was used to transform a yeast strain deficient in recombination and lacking 'X' gene. Transformants, which survive on minimal media and form colonies should essentially have:
Yeast centromeric sequence which ensures integrity of the plasmid after transformation strain
Enchancers for the essential gene missing in transformed strain
A sequence similar to bacterial origin of replication
Yeast autonomous replicating sequence
Following statements have been made about recombination in a diploid organism:
(a) Recombination could be identified by genotyping parents and offsprings for pair loci
(b) Recombination frequency does not exceed o.5, and therefore, 50 cM would be the maximum distance between two loci
(c) Recombination is a reciprocal process. However, a non-reciprocal exchange may cause gene conversion
(d) Ocassionally non-homologous recombination happens and this functions as a source of chromosomal rearrangement.
Select the combination with all correct statements.
(a),(b),(c)
(a),(b),(d)
(b),(c),(d)
(a),(c),(d)
Which one of the following statements true about human chromosomes?
The chromosomes that have highest gene density generally localize towards the centre of the nucleus
The chromosomes that have highest gene density generally localize near the nuclear periphery to facilitate rapid transport of the nascent transcripts
The centromeres of different chromosomes tend to cluster together at the centre of the nucleus
Chromosomal positioning in the nucleus is absolutely random
Three proteins, Blm 1, Blm 2, Blm 3 were shown to be involved in repairs of DNA double strand breaks. A chromatin immuno-precipitation experiment was performed for the three proteins. The pattern of results obtained is shown below:
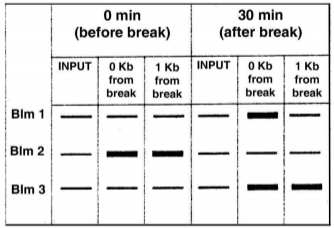
Based on the above figure, choose the option that correctly interpets that data.
Blm 1. Blm 2, Blm 3 bind to DNA break sites
Blm 1 binds to the break sites; Blm 3 binds to he break site and beyond
Blm 2 remains bound to DNA after the break is induced
Blm 3 binds to DNA irrespective of the break
Several mutants (1-4) are isolated, all of which require compund E for growth. The compounds A to D in the biosynthetic pathway to E are known, but their order in the pathway is not known. Each compound is tested for its ability to support the growth of each mutant (1-4). In the following table, a plus sign indicates growth and a minus sign indicateds no growth.
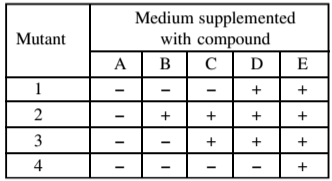
What is the order of the compound (A to E) in the pathway?
E→D→C→B→A
A→C→D→B→E
E→B→D→C→A
A→B→C→D→E
