 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsFor sustained expression of a transgene in the successive generation of a cell line in culture, the ideal gene transfer can be obtained using
Lentiviral vector
Adenoviral vector
Plasmid DNA containing the transgene
Only transgenic DNA
In which of the following techniques does molecular fragmentation offer clues to the covalent chemical structures of biomolecules?
MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry
MALDI-TOF MS/MS mass spectrometry
ESI-TOF MS mass spectrometry
LC-coupled ESI-TOF MS mass spectrometry
The movement of a single cell was required to be continually monitored during development. This cell was marked with a reporter gene. To visualize this movement one would use
Phase contrast Microscopy
Bright field microscopy
Fluorescence microscopy
Atomic force microscopy
The molecular mass of a protein determined by gel filtration is 120 kDa. When its mass is determined by SDS-PAGE with and without β-mercaptoethanol, it is only 60 kDa. What is the most probable explanation for these observations?
Protein is a dimer in which two identical chains are cross linked by disulphide bond(s).
Protein is a monomer of molecular mass 60kDa but it is excluded from the gel matrix due to strong repulsion between the gel matrix and the protein.
Protein is most likely to be composed of two subunits having identical molecular mass.
Protein is a monomer but it is nicked into half its size by SDS.
Mouse IgG isleft wither intact (left lane in A, B, C and D) or digested with papain or pepsin or treated with β-mercaptoethanol (β-ME) and run on non-reducing SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie blue. In a separate experiment, papain-digested products are immunoblottedwith an anti-idiotypic monoclonal antibody. Following four profiles are attributed to each of these treatments.
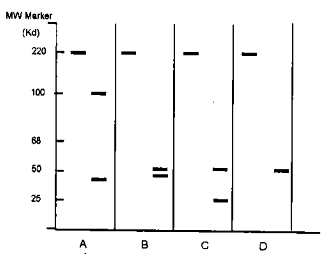
Which one of the following possibilities is correct?
A (pepsin), B (papain), C (β-ME), D (papain, followed by anti-idiotype immunoblot)
A (papain), B (pepsin), C (papain, followed by anti-idiotype immunoblot, D (β-ME)
A (papain, followed by anti-idiotype immunoblot), B (papain), C (Pepsin), D (β-ME)
A (β-ME), B (papain), C (pepsin), D (papain, followed by anti-idiotype immunoblot)
Phosphatidyl serine (PS) is mostly located in the inner bilayer of plasma membrane of red blood cells (RBCs). You have to prove this fact about PS by an experiment. You are provided with PS-specific lytic enzymes (PSE) and other reagents needed.
Identify the correct sequence of experiments to be carried out to settle this issue.
RBCs → inside out vesicles → PSE → Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC)
RBCs → right side out vesicles →TLC → PSE
RBCs → PSE → Inside out vesicles → TLC
RBCs → PSE → TLC → inside out vesicles
A bacterial population has a plasmid with copy number ‘n’. It was observed that on an average in one out of 2(n – 1) cell divisions, there was spontaneous plasmid curing. It was inferred from the observation that :
A. Each cell division does not have equal probability of plasmid curing.
B. There is no evidence for any mechanism of plasmid segregation in the two daughter cells.
C. Plasmid distribution to daughter cells is random.
D. Each plasmid has an equal chance of being in either of the two daughter cells.
Which of the combination of above statements is true?
A and B
B and D
Only A
B, C and D
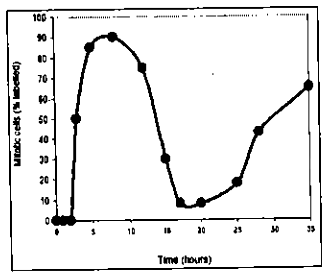
In a given experiment the cells were labeled for 30 minutes with radioactive thymidine. The medium was then replaced with that containing unlabelled thymidine and the cells were grown for additional time. At different time points after replacement of medium the fraction of mitotic cells were analysed. Based on the results obtained, the above figure was drawn which shows the percentage of mitotic cells that are labeled as a function of time after brief incubation with radioactive thymidine.
Considering the above experiment, the following statements were made:
A. Cells in the S-phase of the cell cycle during the 30 minute labeling period contain radioactive DNA.
B. It takes about 3 hours before the first labeled mitotic cells appear.
C. The cells enter the second round of mitosis at t30 hours.
D. The total length of the cell cycle is about 27 hours with G1 being more than 15 hours.
Which of the combinations of the above statements is correct?
A and B
B and C
C and D
A and D
HeLa cell extract was used to study transcription of a gene X having six interns. RNA Pol II complex containing all associated proteins was isolated from actively transcribing system and subjected to proteome. When transcription elongation was inhibited by flavopiridol, polymerase complex contained only capping enzymes. When phosphorylation of the CTD domain of Pol II was inhibited by a kinase inhibitor, the complex contained neither splicing nor capping enzymes. From these results, following conclusions were made:
A. Transcription of gene X is coupled to mRNA capping.
B. Transcription elongation is coupled to splicing.
C. Phosphorylation of CTD is required for the recruitment of capping and splicing enzymes.
D. Both capping and splicing of mRNAs occurs simultaneously.
Identify the correct set of conclusions.
A, B and C
B, C and D
C, D and A
D, A and B
In bacteria, N-formyl methionine is the first amino acid to be incorporated into a polypeptide chain. Accordingly, one would thinl that all bacterial proteins have a formyl group at their amino terminus and the first amino acid is methionine. However, this is not the case, because of the following possible reasons.
A. Deformaylase removes the formyl group.only during or after the synthesis of the polypeptides.
B. Aminopeptidase removes only the amino terminal methionine.
C. Aminopeptidase removes the amino terminal methionine as well as or two additional amino acids.
D. Deformylase removes the formyl group as well as amino terminal methionine and adds one or two amino acids to it.
Choose the combination of correct answers from the following:
B and C
A and B
A and C
A and D
C.
A and C
Among the given statements, statement A and C are correct.
