 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsA protein undergoes post-translational modification. In an experiment to identify the nature of modification, following experimental results were obtained.
A. Protein moved more slowly in an SDS-PAGE.
B. Isoelectric focusing (IEF) showed that there was no change in the pI.
C. Mass spectrometric analysis showed that the modification was on serine.
The modification that the protein undergoes is likely to be
phosphorylation
glycosylation
ubiquitination
ADP-ribosylation
B.
glycosylation
The modification that the protein undergoes is likely to be glycosylation.
During an experiment, a student found increased activity of a protein, for which there were three possible explanations, viz, increased expression of the protein, increased phosphorylation, or increased interaction with other effector proteins. After conducting several experiments, the student concluded that increased activity was due to increased phosphorylation. Which one of the following experiments will NOT support/ provide the correct explanation drawn by the student?
Western blot analysis
Analysis of transcription rate
Mass spectroscopy
Phospho aminoacid analysis
You have transiently expressed a new protein (for which no antibody is available) in a cell line to establish structure-function relationship. Which one of the following strategies is the most straight forward way to examine the expression profile of this new protein?
By metabolic labelling using 35S labelled amino acids.
Making a GFP fusion protein with this new protein.
Immunoprecipitating this protein with the help of another protein for which antibody is available.
Running SDS-PAGE and identify the protein
Fluorescence recovery after photobleaching in live cells is used to determine
co-localization of proteins
distance between two organelles
diffusion of proteins
nucleic acid compactness
A researcher is studying the subcellular localization of a particular protein 'X' in an animal cell. The researcher performs successive centrifugation at increasing rotor speed. The researcher starts spinning the cellular homogenate at 600g for 10 min, collects the pellet, spins the supernatant at 10,000 g for 20 min, collects the pellet, spins the supernatant at 100,000 gm for 1 hour, collects both the pellet and the final supernatant. On subjecting various pellets and the final supernatant to Western blotting with anti-protein-X antibody, the protein X is observed to be maximally expressed in the pellet after centrifugation at 10,000 g. Based on the above observation, what will be the most localization of protein X.
Nucleus
Ribosomes
Mitochondria
Microsomes
Glucose in the blood is detected by four different methods (a, b, c, and d). The sensitivity and range of detection of glucose by these four methods is shown below. Clinically relevant concentration of glucose in blood is between 80 - 250 mg/dL.

Which of the following method is most appropriate?
a
b
c
d
A researcher conducts a standard test to identify enteric bacteria (A, B, C) on the basis of their biochemical properties. The result is given in the following table
| Test | Bacteria A | Bacteria B | Bacteria C |
| Indole | + | - | - |
| Methyl Red | + | + | +/ - |
| Voges-Proskauer | - | - | + |
Based on the above, the identified bacteria A, B, and C are most probably
Enterobacter, Salmonella, Escherichia
Escherichia, Salmonella, Enterobacter
Salmonella, Enterobacter, Escherichia
Escherichia, Enterobacter, Salmonella
You have labelled DNA in a bacterium by growing cells in medium containing either 14N nitrogen or the heavier isotope, 15N. Furthermore, you have isolated pure DNA from these organisms, and subjected it to CsCl density gradient centrifugation leading to their separation of light (14N) and heavy (15N) forms of DNA to different locations in the centrifuge tube. In the next experiment, bacteria were grown first in medium containing 15N, so that all the DNA made by cells will be in heavy form. then these cells will be in heavy form. Then these cells were transferred to medium containing only 14N and allowed the cells to divide for one generation. DNAs were extracted and centrifuged as above in the CsCl gradient. A hybrid DNA band was observed at a position located between and equidistant from the 15N and 14N DNA bands. Based on the above observation, which one of the following conclusions is correct?
The replication of DNA is conservative.
The replication of DNA is semi-conservative.
The replication of DNA is dispersive.
The replication by rolling circle mode
Following is the domain organization of three proteins that are targeted to the mitochondria.
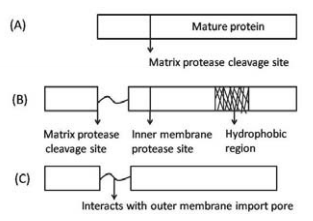
Based on the domain organization in the above figure and assuming the left box to be having the mitochondrial sorting signal, predict the most likely sub-compartment of the mitochondria in which the protein will be found.
A in matrix; B in inner membrane; C in inter-membrane space.
A in inner membrane; B in inter-membrane space; C in outer membrane.
A and B are in matrix; C in outer membrane.
A in` matrix; B and C are in inter-membrane space.
Four single amino acid mutants (a to d) of a protein in the epitope-region of a monoclonal antibody X were made and expressed in E. coli. The lysates from the four E. coli cultures expressing these four proteins were run or an SDS-PAGE gel and subsequently transferred to nitrocellulose membrane and Western blotted using a monoclonal antibody X raised against the wild type protein. The results are presented in the figure below.
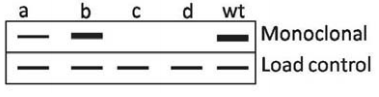
The four single mutation, upon sequencing, were found to be Valine (V) to Alanine(A); Glycine (G) to Proline (P); Alanine (A) to Aspartic acid (D) and isoleucine (I) to Leucine (L).
Which one of the following statements is correct?
b is due to V → A and c is sue to G → P
b is due to G → P and d is due to V → A.
d is due to I → L and a is due to A → D.
c is due to V → A and a is due to I → L.
