 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsWhich one of the following options correctly relates the source gland/ organ with its respective hormone as well as function?
| Source gland | Hormone | Function |
| Thyroid | Thyroxine | Regulates blood calcium level |
| Anterior pituitary | Oxytocin | Contraction of uterine muscles |
| Posterior pituitary | Vasopressin | Resorption of water in distal tubules of the nephron |
| Corpus luteum | Estrogen | Supports pregnancy |
C.
| Posterior pituitary | Vasopressin | Resorption of water in distal tubules of the nephron |
The correct match is-
Posterior pituitary - Vasopressin - Resorption of water in distal tubules of nephron.
Action potentials were recorded intracellularly from different parts of mammalian heart and these are shown below. Which one of these has been recorded from the sinoatrial node?
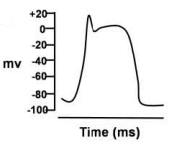
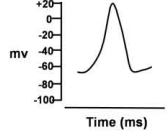
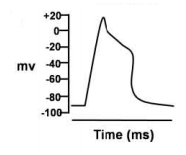
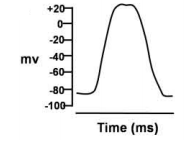
The membrane potential in a giant squid axon recorded intracellularly at the resting condition (-70 mV) was reversed at the peak of action potential (+35 mV) after stimulation of the nerve fibre with a threshold electrical stimulus. This overshoot of the membrane potential has been explained in the following proposed statements:
A. The rapid increase in Na+-conductance during earl phase of action potential causes membrane potential to move toward the equilibrium potential of Na+ (+45 mV).
B. The Na+-conductance quickly decreases toward resting level after peak in the early phase and Na+-ions are not able to attain its equilibrium potential within this short time.
C. The conductance of K+ at the early phase of action potential is increased and that leads to the reversal of membrane potential.
D. The increase of K+-conductance due to stimulation of nerve occurs before the changes of Na+-conductance is initiated and thus causes overshoot at the peak of action potential.
Which one of the following is correct?
A only
A and B
C only
C and D
A majority of humans with normal colour vision was found to be more sensitive to red light in Rayleigh match where the subject mixed variable amount of red and green light to match monochromatic orange. Which one of the following statements is NOT true to explain the observation?
There are variations in the sensitivity of long-wave cone pigments.
The short-wave cone opsin in red-sensitive subjects is different from others.
The absorption curve of long-wave cone pigment peaks at 556 nm in red-sensitive subjects while it peaks at 552 nm in others.
The long-wave cone opsin in red-sensitive subjects is different in primary structure from that of others.
Dose-dependent of retinoic acid treatment supports the notion that a gradient of retinoic acid can act as a morphogen along the proximo-distal axis in a developing limb. The following are certain facts related to the above notion.
A. Treatment with a high level of retinoic acid causes a proximal blastema to be respecified as a distal blastema and only distal structures are regenerated.
B. Treatment with a high level of retinoic acid causes a distal blastema to be respecified as a proximal blastema and regeneration of a full limb may be initiated.
C. Treatment with retinoic acid affects only distal blastemas and causes them to form only proximal structures.
D. Treatment with high level of retinoic acid causes any blastema to form only distal structures.
Which one of the following is correct?
B and D
Only C
A and C
Only B
The cell bodies of sympathetic preganglionic neurons are located in:
intermediolateral cell column of spinal cord.
Posterior cell column of spinal cord
Celiac ganglion
Paravertebral ganglion
Excess oxygen consumed after a vigorous exercise is
to pump out lactic acid from muscle
to increase the concentration of lactic acid in muscle.
to reduce dissolved carbon dioxide in the blood.
to make ATP for gluconeogenesis
Serum has essentially the same composition as plasma except that it lacks
Albumin
Stuart-Prower factor
Antihemophilic factor
Hageman factor
Vasopressin secretion does NOT increase with
exercise
an increase in extracellular fluid volume
standing
vomiting
Which type of cells located in gastric glands is responsible for the release of histamine?
Mucous neck cells
Enterochromaffin-like cells
Chief cells
Parietal cells
