 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsThree anatomical characteristics (A, B and C) of invertebrate nervous system are used to build a generalized cladogram given below. Presence of the anatomical character is indicated by ‘+’
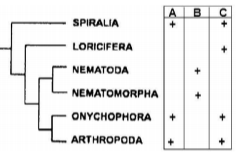
Based on the pattern of character distribution, pick the correct combination that are represented by A, B and C
A-unpaired nerve cord, B-paired nerve cord, C-cephalic ganglia
A-cephalic ganglia, B-unpaired nerve cord, C-paired nerve cord
A-cephalic ganglia, B-paired nerve cord, C-unpaired nerve cord D
A-unpaired nerve cord, B-cephalic ganglia, C-paired nerve cord.
The following table shows names of bones (column A) and specific features (column B)
| Column A | Column B |
| (a) Axis vertebra | (i) Deltoid Ridge |
| (b) Humerus | (ii) Acromion Process |
| (c) Ulna | (iii) Odontoid Process |
| (d) Pectoral girdle | (iv) Sigmoid Notch |
Which one of the following options gives the correct match of the bones with their specific features?
| (a) | (b) | (c) | (d) |
| (iii) | (i) | (iv) | (ii) |
| (a) | (b) | (c) | (d) |
| (ii) | (i) | (ii) | (iv) |
| (a) | (b) | (c) | (d) |
| (iv) | (ii) | (i) | (iii) |
| (a) | (b) | (c) | (d) |
| (i) | (iii) | (iv) | (ii) |
The figure below shows the nervous system of Mollusca with ganglia and the connecting nerves. The connecting nerves are labelled as A, B, C and D.
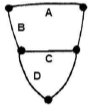
Which one of the following options has correct labelling of A, B, C and D?
A-Cerebral commissure; B-Left Cerebropedal connective; C-Pedal commissure; D-Left Pedal-visceral connective
A-Cerebral connective; B-Left Cerebropedal commissure; C-Pedal connective; D-Left Pedal-visceral commissure
A-Occipital commissure; B-Occipito-pedal connective; C-Pedal commissure; D-Left Pedo-caudal connective
A-Cerebral connective; B-Left Cerebropedal commissure; C-Pedal commissure; D-Pedal-caudal connective
Four drugs (A, B, C, D) were used a biological rhythm in experimental animals. The changes in the pattern of the biological rhythm as compared to untreated are shown below. The solid line represents the biological rhythm of the untreated and broken line represents that of the treated animals.
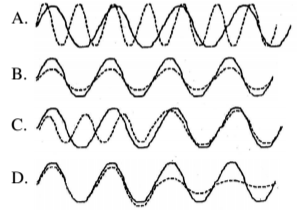
Which of the following interpretations from the above experiments is incorrect?
Drugs A can be used to reduce the period lenght of the rhythm
Drugs B can be used for sustained lowering of amplitude of the rhythm without changing its period
Drugs C can be used for sustained lowering of amplitude and periods of the rhythm
Drugs D can be used to reduced the robustness and dampen out the rhythm.
The conduction velocity of action potential in a myelinated nerve fibre was much greater than that of an unmyelinated fibre of the same diameter. The following statements were proposed to explain this observation:
(a) The speed of conduction in a nerve fibre is determined by the plasma membrane resistance and axial resistance and axial resistance of axonal cytoplasm.
(b) The electrical properties of myelinated and unmyelinated nerve fibres are not similar.
(c) The myelin sheath decreases the effective membrane resistance.
(d) The magnitude of an electrotonic potential decreases more with distance along the axon in myelinated nerve fibres than that of unmyelinated fibres.
(e) The voltage-gated Na+ channels are highly concentrated at the nodes of Ranvier.
Choose one of the following combinations with both INCORRECT statements.
(a) and (b)
(b) and (c) only
(c) and (d) only
(d) and (e) only
C.
(c) and (d) only
Both membrane and axonal resistance is required to calculate the speed of conductance. Statement (a) is true.
Myelin has both passive and active properties: It increases the axon's membrane capacitance. Statement (b) is true and (c) is false.
The movement of sodium ions to depolarize the membrane can only occur at the Node of Ranvier, as the sodium voltage-gated channels are found only at the nodes of Ranvier. Statement (e) is correct.
A four year old boy was brought to hospital for weak boes in spite of sufficient intake of calcium in his diet. The attending doctor examined the functioning of the following organs:
(a) Liver (b) Kidney
(c) Lung (d) Pancreas
Which one of the following options represents a combination of probable malfunctioning organs?
(a) and (b)
(b) and (c)
(c) and (d)
(a) and (d)
The oxygen-haemoglobin dissociation curve illustrates the relationship between pO2 in blood and the number of O2 molecules bound to haemoglobin. The 'S' shape of the curve has been explained in the following proposed statements:
(a) The quaternary structure of haemoglobin determines its affinity to O2.
(b) In deoxyhaemoglobin, the globin units are tightly bound in a T-configuration.
(c) The interactions between globin subunits are altered when O2 binds with deoxyhaemoglobin.
(d) The affinity to O2 in T-configuration of haemoglobin is increased.
(e) In the relaxed configuration of haemoglobin, the affinity to O2 is reduced.
Choose one of the following combinations with both INCORRECT statements.
(a) and (b)
(b) and (c)
(c) and (d)
(d) and (e)
The changes in left atrial, left ventricular and aortic pressure in a cardiac cycle are shown below in the figure:
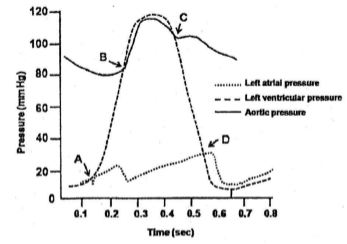
Given below are the events of cardiac cycle (Column A) associated with marked points (A, B, C, D) in the figure (Column B).
| Column A | Column B | |
| (a) | Aortic valveopens | (i) D |
| (b) | Mitral valve closes | (ii) B |
| (c) | Mitral valve opens | (iii) A |
| (d) | Aortic valve closes | (iv) C |
Choose the option that matches the events with marked points in the figure:
| (a) | (b) | (c) | (d) |
| (ii) | (iii) | (i) | (iv) |
| (a) | (b) | (c) | (d) |
| (i) | (iv) | (iii) | (ii) |
| (a) | (b) | (c) | (d) |
| (iv) | (i) | (iii) | (ii) |
| (a) | (b) | (c) | (d) |
| (iii) | (ii) | (iv) | (i) |
A person recovered from a moderate degree of haemorrhagic shock. The participating physiological mechanisms in this recovery process are proposed in the following statements.
(a) The decrease in arterial pressure after haemorrhage causes inhibition of symphathetic-vasoconstrictor system.
(b) After haemorrhage, the angiotensin II level in blood is increased which causes increased re-absorption of Na+in renal tubules.
(c) The increased secretion of vasorpressin after haemorrhage increases water retention by the kidneys.
(d) After haemorrhage, the reduced secretion of epinephrine and nor-epinephrine from adrenal medulla induces decreased peripheral resistance.
(e) In haemorrhage, the central nervous system ischemic response elicits sympathetic inhibition.
Choose one of the following combinations with both the correct statements.
(a) and (b)
(b) and (c)
(c) and (d)
(d) and (e)
A healthy individual was immersed in water up to neck in an upright posture for 3h. The plasma concentration of atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP), renin and aldosterone were measured for 5h at 1h intervals including the immersion periods. The result are graphically presented below.
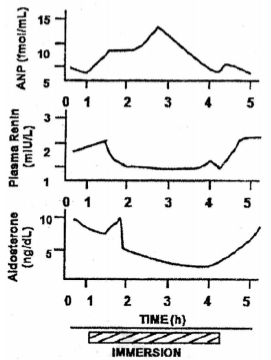
The result pf this experimental condition (EC) are explained in the following proposed statements which may be corrected or incorrected.
(a) ANP secretion is proportional to the degree of stretch of atria.
(b) The decreased plasma renin concentration in EC is due to increase in sympathetic activity.
(c) The decreased aldosterone level in EC is the effect of plasma renin level.
(d) The effect of gravity on the circulation is counteracted in EC.
(e) The central venous pressure is decreased in EC.
Chose one of the following combination with all correct statements.
(a), (b), (c)
(a), (c), (d)
(c), (d), (e)
(b), (c), (d)
