 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsSieve elements of phloem conduct sugars and other organic materials throughout the plant. The following statements were made about characteristics of sieve elements in seed plants:
(a) Angiosperms contain sieve plant pores.
(b) There are no sieve plates in gymnosperms.
(c) P-protein is present in all eudicots and many monocots.
(d) There is no P-protein in angiosperms.
Which of the following combinations is correct?
(b), (c) and (d)
(a), (b) and (c)
(a), (b) and (d)
(a), (c) and (d)
The plant hormones, auxins and cytokinins, and their interactions play an important role in regulating apical dominance. The following figure represents an experiment related to the study of gene interactions that influence axillary bud outgrowth or dormancy. Q,Z and M represent genes involved in phytohormone pathway.
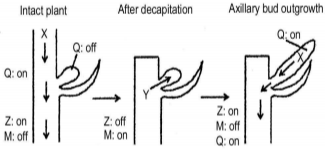
Based on the above figure, the following statements were made:
(a) 'X' is an auxin that maintains expression of 'Q' and 'Z' and represses 'M'.
(b) 'Y' is a cytokinin that promotes axillary bud growth and is induced by 'M'.
(c) Decapitation (removal of apex) activates 'X'.
(d) 'X' is a cytokinin that represses 'M'.
Which one of the following options reprsents correct statement(s)?
(a) and (c) only
(b) and (d) only
(a) and (b) only
(c) only
C.
(a) and (b) only
In many plants the growing shoot apex inhibits the outgrowth of axillary buds, a phenomenon termed 'apical dominance'. Removal of the shoot apex leads to the release of dormant axillary buds below it form branches. Apical dominance allows plants to focus resources into the main axis of growth, while activation of dormant buds allows for recovery after damage or loss of the main shoot. It has been known for long time that auxin is a major signal for apical dominance. If auxin is applied to a decapitated stump at the shoot apex, it can replace the growing apex in restoring branch inhibition. Auxin is mainly synthesized in the shoot apex in young leaves and subsequently transported basipetally (downwards from the tip to the base) in the polar auxin transport stream (PATS), Cytokinins represent a possible second messenger for auxin signalling in regulating bud activity. Endogenous CKs can be transported acropetally (towards the shoot apex) in the xylem sap, enter axillary buds and promote their outgrowth.
Following table shows presences (+) and absences (-) of selected distinguishing characters of different plant taxa:
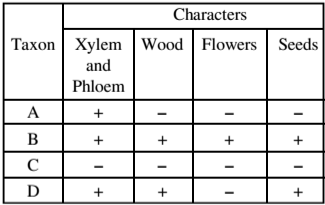
Based on the above, which of the following shows correct identity of taxa A,B, C and D?
A-Hornworts; B-Oaks; C-Ferns; D-Pines
A-Ferns; B-Oaks; C-Hornworts; D-Pines
A-Hornworts; B-Pines; C- Ferns; D-Oaks
A-Ferns; B-Pines; C- Hornworts; D- Oaks.
Completed the following sentences with the most appropriate option.
Global analysis of a larger number of plant species traits showed that with increase in leaf life spa.
Specific leaf area increases whereas leaf nitrogen and net photosynthesis rate decrease.
Specific leaf area, leaf nitrogen and net photosynthesis rate increase
Specific leaf area, leaf nitrogen and net photosynthesis rate decrease.
Specific leaf area decrease whereas leaf nitrogen and net photosynthesis rate increase.
Which of the following mineral deficiency will first be visible in younger leaves?
Calcium
Nitrogen
Zinc
Molybdenum
The CO2 compensation poibt for C3 plants is greater than C4 plants because in C3 plants
Dark respiration is higher
Dark respiration is lower
Photorespiration is present
Photorespiration is absent
Which one of the following best describes the function of Casparian bands during the translocation of nutrients and water across the root?
Block apoplastic nutrient transport
Block symplastic nutrient transport
Act as a nutrient carrier
Help in creating passage cells
Which one of the following components is expected to be most abdundant in phloem sap of a plant?
Proteins
Organic acids
Sugars
Phosphates
Basal angiosperms are NOT represented by the members of:
Chloranthales
Nymphaeales
Austrobaileyales
Amborellales
