 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsAmongst the following compounds, the one(s) which readily react with ethanolic KCN.
Ethyl chloride
Chlorobenzene
Benzaldehyde
Salicylic acid
An amine C3H9N reacts with benzene sulphonyl chloride to form a white precipitate which is insoluble in aq. NaOH. The amine is


![]()

The reaction of aniline with chloroform under alkaline conditions leads to the formation of
phenylcyanide
phenylisonitrile
phenylcyanate
phenylisocyanate
When aniline is nitrated with nitrating mixture in ice cold condition, the major product obtained is
p-nitroaniline
2,4-dinitroaniline
o-nitroaniline
m-nitroaniline
The basicity of aniline is weaker in comparison to that of methyl amine due to
hyperconjugative effect of Me-group in MeNH2
resonance effect of phenyl group in aniline
lower molecular weight of methyl amine as compared to that of aniline
resonance effect of - NH2 group in MeNH2
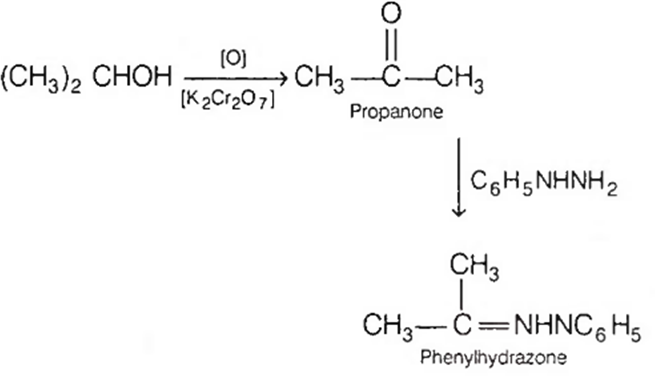
An organic compound X is oxidised by using acidified K2Cr2O7. The product obtained reacts with phenyl hydrazine, but does not answer silver mirror test. The possible structure of X is
CH3COCH3
(CH3)2CHOH
CH3CHO
CH3CH2OH
B.
(CH3)2CHOH
The oxidation product of X reacts with phenyl hydrazine, thus it contains >C=O group. The same product does not (give) silver mirror test. Thus, it is a ketone, because only aldehydes give silver mirror test.
Thus, the compound X must be 2° alcohol, as only secondary alcohols give ketones on oxidation and hence, X is (CH3)2CHOH.
The increasing order of the rate of HCN addition to compound A-D is
A. HCHO B. CH3COCH3
C.PhCOCH3 D. PhCOPh
A< B < C < D
D< B< C< A
D < C < B < A
C < D< B< A
