 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsA hypothetical reaction A 2B proceeds through the following sequence of steps
I. A C;
II. C D;
III. B;
The heat of hypothetical reaction is
q1 + q2 - 2q3
q1 + q2 + 2q3
q1 + 2q2 - 2q3
q1 - q2 + 2q3
Look at the graph,
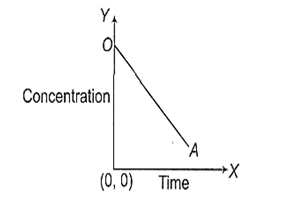
Choose the correct equation from the following which best suited to the above graph
[At] = [A]0 -Kt
[At] = [A]0 + Kt
[At] = [A0]e-Kt
[At] = Kt2 + [A0]
Observe the following reaction
2A + B C
The rate of formation of C is 2. 2 x 10-3 mol L-3 min-1. What is the value of (in mol L-1 min-1)?
Which of the following is an example for heterogeneous catalysis reaction?
2SO2(g) + O2 2SO3(g)
Hydrolysis of aqueous sucrose solution in the presence of a aqueous mineral acid
2H2O2 (l) 2H2O2(l) + O2(g)
Hydrolysis of liquid in the presence of aqueous mineral acid
A hypothetical reaction
X2 + Y2 2XY follows the following mechanism
X2 X + X .... fast
X + Y2 XY + Y .... slow
X + Y XY .... fast
The order of overall reaction is
2
1
0
The variation of concentration of the product P with time in the reaction, A P is shown in following graph.

The graph between and time will be of the type

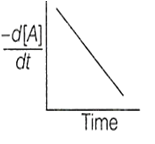


A.

According to the graph given in the question, the graph between will be of type a.
Concentration of the product increases lineraly with time t, thus order = 0 and = constant.
The average kinetic energy of an ideal gas per molecule in SI units at 25°C will be
6.17 x 10-21 JK-1
6.17 x 10-21 JK-1
6.17 x 1020 JK-1
7.16 x 10-20 JK-1
In the first order reaction, 75% of the reactant gets disappeared in 1.386 h. The rate constant of the reaction is
3.0 10-3 s-1
2.8 10 -4 s-1
17.2 10-3 s-1
1.8 10-3 s-1
2 g of a radioactive sample having half-life of 15 days was synthesised on 1st Jan 2009. The amount of the sample left behind on 1st March, 2009 (including both the days) is
0 g
0.125 g
1 g
0.5 g
