 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice Questions1 g of a non-volatile non – electrolyte solute is dissolved in 100 g of two different solvents A and B whose ebulliscopic constants are in the ratio of 1:5. The ratio of the elevation in their boiling points, is:
1:0.2
10: 1
5: 1
1: 5
A 1000C the vapour pressure of a solution of 6.5 g of a solute in 100 g water is 732 mm. If Kb = 0.52, the boiling point of this solution will be
1000C
1020C
1030C
1030C
Which of the following statements about the composition of the vapour over an ideal 1:1 molar mixture of benzene and toluene is correct? Assume that the temperature is constant at 250C.
(Given, vapour pressure data at 250C benzene = 12.8 kPa, toluene = 3.85 kPa)
The vapour will contain a higher percentage of toluene
The vapour will contain equal amounts of benzene and toluene
Not enough information is given to make a prediction
Not enough information is given to make a prediction
A mixture of gases contains H2 and O2 gases in the ratio of 1:4 (w/w).what is the molar ratio of the two gases in the mixture?
1:4
4:1
16:1
16:1
B.
4:1
Let the mass of H2 gas be x g and mass of O2 gas 4x g
Molar H2 : O2
mass 2 : 32
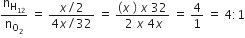
The boiling point of 0.2 mol kg-1 solution of X in water is greater than the equimolal solution of Y in water. Which one of the following statements is true is this case?
X is undergoing dissociation in water
The molecular mass of X is greater than the molecular mass of Y.
Molecular mass of X is less than the molecular mass of Y,
Molecular mass of X is less than the molecular mass of Y,
Which one of the following electrolytes has the same value of van't Hoff's factor (i) as that of Al2(SO4)3 (if all are 100% ionised)?
K2SO4
K3[Fe(CN)6]
Al(NO3)3
Al(NO3)3
In Duma's method for estimation of nitrogen 0.25 g of an organic compound gave 40 ml of nitrogen collected at 300 K temperature and 725 mm pressure. If the aqueous tension at 300 K is 25 mm the percentage of nitrogen in the compounds is,
17.36
18.20
16.76
15.76
Of the following 0.10 m aqueous solutions, which one will exhibit the largest freezing point depression?
KCl
C6H12O6
Al2(SO4)3
Al2(SO4)3
The weight of silver (at. wt. = 108) displaced by a quantity of electricity which displaces 5600 mL of O2 at STP will be
5.4 g
10.8 g
54.0 g
54.0 g
