 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsA wire of resistance 4Ω is stretched to twice its original length. The resistance of stretched wire would be
2Ω
4Ω
8Ω
8Ω
The internal resistance of a 2.1 V cell which gives a current of 0.2 A through of 0.2A through a resistance of 10Ω is
0.2Ω
0.5Ω
0.8Ω
0.8Ω
The resistance of the four arms P, Q, R and S a Wheatstone's bridge are 10Ω, 30Ω and 90Ω respectively. The emf and internal resistance of the cell are 7V and 5Ω respectively. If the galvanometer resistance is 50Ω, the current drawn from the cell will be
1.0 A
0.2 A
0.1 A
0.1 A
If power dissipated in the 9Ω resistor in the circuit shown is 36 W, the potential difference across the 2Ω resistor is

8 V
10 V
2 V
2 V
A current 2 A flows through a 2 Ω resistor when connected across a battery. The same battery supplies a current of 0.5 A when connected across a 9 Ω resistor. The internal resistance of the battery is
1/3 Ω
1/4 Ω
1 Ω
1 Ω
A uniform electric field and a uniform magnetic field are acting along the same direction in a certain region. If an electron is projected in the region such that its velocity is pointed along direction of fields, then the electron
speed will decrease
speed will increase
will turn towards the left of the direction of motion
will turn towards the left of the direction of motion
A circuit contains an ammeter, a battery of 30 V and a resistance 40.8 Ω all connected in series. If the ammeter has a coil of resistance 480 Ω and a shunt 20 Ω then reading in the ammeter will be
0.5 A
0.25 A
2 A
2 A
A potentiometer wire of length L and a resistance r are connected in series with battery of e.m.f. Eo and a resistance r1. An unknown e.m.f is balanced at a length l of the potentiometer wire. The e.m.f E will be given by
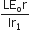
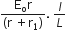
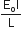
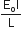
A square loop, carrying a steady current I, is placed in a horizontal plane near a long straight conductor carrying a steady current I1 at a distance d from the conductor as shown in the figure. The loop will experience
a net repulsive force away from the conductor
a net torque acting upward perpendicular to the horizontal plane
a net torque acting downward normal to the horizontal plane
a net torque acting downward normal to the horizontal plane
In the circuit shown in the figure, if potential at point A is taken to be zero,the potential at point B is
-1V
+2 V
-2 V
-2 V
