 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsA ray of light is incident at an angle of incidence, i, on one face of the prism of angle A (assumed to be small) and emerges normally from the opposite face. If the refractive index of the prism is u, the angle of incidence i, is nearly equal to

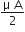

If the focal length of the objective lens is increased, then the magnifying power of,
microscope will increase but that of telescope will decrease
microscope and telescope both will increase
microscope and telescope both will decrease
microscope and telescope both will decrease
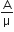
The angle of a prism is A. One of its refracting surfaces is silvered. Light rays falling at an angle of incidence 2A on the first surface returns back through the same path after suffering reflection at the silvered surface. The refractive index  , of the prism is,
, of the prism is,
2 sin A
2 cos A
1/2 cos A
1/2 cos A
For a normal eye, the cornea of eye provides a converging power of 40 D and the least converging power of the eye lens behind the cornea is 20 D. Using this information, the distance between the retina and the cornea eye lens can be estimated to be
5 cm
2.5 cm
1.67 cm
1.67 cm
A plano-convex lens fits exactly into a Plano-convex lens. Their plane surfaces are parallel to each other. If lenses are made of different materials of refractive indices  and
and  and R is the radius of curvature of the curved surface of the lenses, then the focal length of the combination is
and R is the radius of curvature of the curved surface of the lenses, then the focal length of the combination is




A biconvex lens has a radius of curvature of magnitude 20 cm. Which one of the following options describes best the image formed on an object of height 2 cm placed 30 cm from the lens?
Virtual, upright, height = 0.5 cm
Real, invented, height = 4 cm
Real, inverted, height = 1 cm
Real, inverted, height = 1 cm
In an astronomical telescope in normal adjustment, a straight black line of length L is drawn on inside part of the objective lens. The eye - piece forms a real image of this line. The length of this image is I. The magnification of the telescope is
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
A beam of light consisting of red, green and blue colours is incident on a right-angled prism. The refractive index of the material of the prism for the above red, green and blue wavelength are 1.39, 1.44 and 1.47

The Prism will
separate the blue colour part from the red and green colours
separate all the three colours from one another
not separate the three colours at all
separate the red colour part from the green and blue colours
A thin prism of angle 15o made of glass of refractive index is combined with another prism of a glass of refractive index.
combined with another prism of a glass of refractive index. The combination of the prism produces dispersion without deviation. The angle of the second prism should be
The combination of the prism produces dispersion without deviation. The angle of the second prism should be
7o
10o
12o
12o
A conversing beam of rays is incident on a diverging lens. Having passed though the lens the rays intersect at a point 15 cm from the lens on the opposite side. If the lens is removed the point where the rays meets will moves 5 cm closer to the lens. The focal length of the lens is
-10 cm
20 cm
-30 cm
-30 cm
C.
-30 cm
Given u = 10 cm, v = 15 cm
