 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsAssertion: The clouds in sky generally appear to be whitish.
Reason: Diffraction due to clouds is efficient in equal measure at all wavelengths.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false
Sodium lamps are used in foggy conditions because
yellow light is scattered less by the fog particles
yellow light is scattered more by the fog particles
yellow light is unaffected during its passage through the fog
wavelength of yellow light is the mean of the visible one
A monochromatic beam of light is used for the formation of fringes on the screen by illuminating the two slits in the Young's double slit interference experiment. When a thin film of mica is interposed in the path of one of the interfering beams then
the fringe width increases
the fringe width decreases
the fringe width remains the same but the pattern shifts
the fringe pattern disappears
When a compact disc is illuminated by a source of white light, coloured lines are observed. This is due to
dispersion
diffraction
interference
refraction
Assertion: At the first glance, the top surface of the Morpho butterfly's wing appears a beautiful blue-green. If the wing moves the colour changes.
Reason: Different pigments in the wing reflect light at different angles.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false
Assertion: A famous painting was painted by not using brush strokes in the usual manner, but rather a myriad of small colour dots. In this painting the colour you see at any given place on the painting changes as you move away.
Reason: The angular separation of adjacent dots changes with the distance from the painting.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false
Assertion: Crystalline solids can cause X-rays to diffract.
Reason: Interatomic distance in crystalline solids is of the order of 0.1 nm.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false
When a beam of light is used to determine the position of an object, the maximum accuracy is achieved if the light is
polarised
of longer wavelength
of shorter wavelength
of high intensity
A double slit experiment is performed with light of wavelength 500 nm. A thin film of thickness 2 μm and refractive index 1.5 is introduced in the path of the upper beam. The location of central maximum will
remain unshifted
shift downward by nearly two fringes
shift upward by nearly two fringes
shift downward by 10 fringes
C.
shift upward by nearly two fringes
Wavelength λ = 500 nm = 500 × 10-9 m
Thickness of the film t = 2 μm = 2 × 10-6 m
Refractive index μ = 1.5
Where there is no thin film placed in the path of any one of the two beams, the path difference between them is given by dy/D ( considering the two beams meetings at a point P ). In case we put a thin film in the path of one of the beams, then the optical path of that beam gets longer.
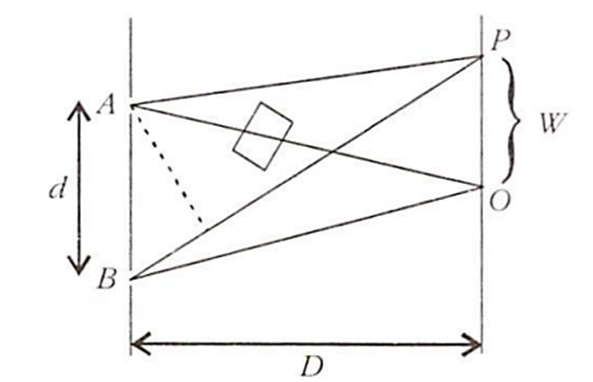
Now for the central maximum, path difference in the absence of the film is Δx = 0. But when we put the film, the path difference becomes
Δx = μt t
= ( μ 1 ) t
= ( 1.5 1 ) × 2 × 10-6
= 10-6
Δx = 1 mm
Now,
Δx =
⇒ y = Δx
⇒ y = × 0.5 × 1 μm
⇒ = 2 × × 1 μm
⇒ y = 2 W
As the film is placed in the path of the upper beam the cenr=tral maximum will shift upward by nearly two fringes.
Assertion: The stars twinkle while the planets do not.
Reason: The stars are much bigger in size than the planets.
if both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion
if both assertion and reason are true and the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion
if assertion is true but reason is false
if both assertion and reason are false statements
