 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsStudy the following statements.
I. F1 -progeny is the first hybrid generation and progeny resembles either of the two
parents.
II. F2 progeny is a resultant hybrid generation of cross pollination among F1 progeny and progeny shows retain as such both drawf and tall plants.
III. F2 progeny is second hybrid generation, produced by selfing F1 hybrids and progeny contained both drawf and tall plants.
IV. The proportion of probability of plants that were drawf were 1/4th of the F2 plants while 3/4th of the F2 plants were tall.
The correct statements are
I, II, III, IV
I, III, IV
I, II, IV
III, IV
In sweet pea, C and P genes are essential for flower colour. In absence of either or both the genes, the flowers are white. What will be the percentage of coloured flowers in the offspring of cross Ccpp x ccPp?
75%
25%
80%
50%
B.
25%
The mentioned cross in the question is a dihybrid.
Ccpp x ccPp (both are white)
Hence, ratio of coloured to white flowers is 1:3.
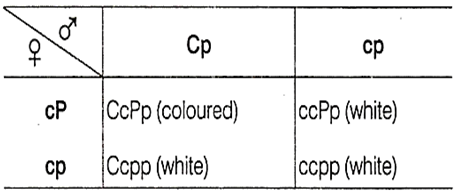
Therefore, the percentage of coloured flowers in offsprings is 25%.
A women with albinic father marries an albinic man. The proportion of her progeny is
2 normal : 1 albinic
All normal
All albinic
1 normal : 1 albinic
Who formulated the chromosomal theory of linkage
T H Morgan and W Castle
Stern and Hotta
Pontecarvo
Bridges and Burns
A pea with white flower was crossed with another pea with white flower. When they selfed, the F2 generation produced purple and white in the ratio of 9:7. The reason for the result is that
it is typical monohybrid Mendelian ratio
purple flower colour is dominant over white
it is a complementary factor
None of the above
The gene controlling seven traits in pea studied by Mendel were later found to be located on the following number of chromosomes
seven
four
five
six
The crossing of a homozygous tall pea plant and homozygous dwarf pea plant would yield plants in the ratio of
2 tall : 2 dwarf
all heterozygous tall
all homozygous dwarf
one homozygous tall; one homozygous dwarf; two heterozygous tall
The offsprings obtained by mating two pure strains having constrasting characters are called as
mutants
hybrids
F2 - generation
P - generation
What is not true about alleles?
Round and wrinkled form of genes are alleles of each other
Only recessive alleles expreses in hybrid
Alleles occupy same loci on homologous chromosomes
Two or more alternative forms of gene are called alleles are allelomorphs
In Mendelian monohybrid cross, phenotypic ratio in F2 is 3 :1. How many types of gametes are formed in F1 -generation?
Two types
Four types
Eight types
Only one types
