 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsThe correct sequence of reactions to be performed to convert benzene into m-bromoaniline is
nitration, reduction, bromination
bromination, nitration, reduction
nitration, bromination, reduction
reduction, nitration, bromination
The correct statement is
Cyclohexadene and cyclohexene cannot be isolated with ease during controlled hydrogenation of benzene
One mole each of benzene and hydrogen when reacted gives 1/3 mole of cyclohexane and 2/3 mole unreacted hydrogen
Hydrogenation of benzene to cyclohexane is an endothermic process
It is easier to hydrogenate benzene when compared to cyclohexene
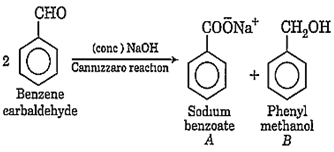
Benzene carbaldehyde is reacted with conc. NaOH solution to give the products A and B. The product A can be used as a food preservative and the product B is an aromatic hydroxy compound, where -OH group is linked to sp3-hybridised C-atom next to benzene ring. The products A and B respectively are
sodium benzoate and phenol
sodium benzoate and phenyl methanol
sodium benzoate and cresol
sodium benzoate and picric acid
B.
sodium benzoate and phenyl methanol
When benzene carbaldehyde reacts with NaOH, it proceeds via Cannizzaro reaction. It is a disproportionation reaction in which half of the molecules of aldehyde are oxidised and other half are reduced.
The arrangement of following compounds.
(i) Bromomethane
(ii) Bromoform
(iii) Chloromethane
(iv) Dibromomethane
In the increasing order of their boiling point is
III < I < IV < II
IV < III < I < IV
II < III < I < IV
I < II < III < IV
An organic compound A on reduction gives compound B, which on reaction with trichloromethane and caustic potash forms C. The compound C on catalytic reduction gives N-methyl benzenamine, the compound A is,
nitrobenzene
nitromethane
methanamine
benzenamine
Which of the following has highest knocking ?
Olefins
Branched chain olefins
Straight chain olefins
Aromatic hydrocarbons
Chlorination of benzene is not possible in the following reaction :
C6H6 + Cl2
C6H6 + HOCl
C6H6 + I-Cl
C6H6 + Cl2
In which of the following, homolytic bond fission takes place?
Free radical chlorination of methane
Addition of HBr to double bond
Alkaline hydrolysis of ethyl chloride
Nitration of benzene
A petroleum fraction having boiling range 70-200°C and containing 6-10 carbon atoms per molecule is called :
natural gas
gas oil
gasoline
kerosene
