 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsA proton and a deuteron with the same initial kinetic energy enter a magnetic field in a direction perpendicular to the direction of the field. The ratio of the radii of the circular trajectories described by them is
1 : 4
1 : 1
1 : 2
Two tangent galvanometers A and B have coils of radii 8 cm and 16 cm respectively and resistance 8 Ω each. They are connected in parallel wth a cell of emf 4 V and negligible internal resistance. The deflections produced in the tangent galvanometers A and B are 30° and 60° respectively. If A has 2 turns, then B must have
18 turns
12 turns
6 turns
2 turns
A charged particle is moving in a magnetic field of strength B perpendicular to the direction of the field. If q and m denote the charge and mass of the particle respectively, then the frequency of rotation of the particle is
The magnetic field at the centre of a circular current carrying conductor of radius r is Bc. The magnetic field on its axis at a distance r from the centre is Ba. The value of Bc : Ba wil be
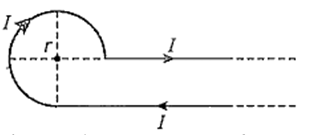
Current I is flowing in conductor shaped as shown in the figure. The radius of the curved partis r and the length of straight portion is very large. The value of the magnetic field at the centre O will be
Two tangent galvanometers A and B are identical except in their number of turns. They are connected in series. On passing a current through them, deflections of 60° and 30° are produced. The ratio of the number of turns in A and B is
1 : 3
3 : 1
1 : 2
2 : 1
A certain current on passing through a galvanometer produces a deflection of 100 divisions. When a shunt of one ohm is connected, the deflection reduces to 1 division. The galvanometer resistance is
100 Ω
99 Ω
10 Ω
9.9 Ω
B.
99 Ω
Shunt is connected to the galvanometer
A direct current I flows along the length of an infinitely long straight thin walled pipe, then the magnetic field is
uniform throughout the pipe but not zero
zero only along the axis of the pipe
zero at any point inside the pipe
maximum at the centre and minimum at the edge
A galvanometer of resistance 240 Ω allows only 4% of the main current after connecting a shunt resistance. The value of the shunt resistance is
10 Ω
20 Ω
8 Ω
5 Ω
A coil of n number of turns is wound tightly in the form of a spiral with inner and outer radii a and b respectively. When a current of strength is passed through the coil, the magnetic field at its centre is
