 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsA thin plano-convex lens acts like a concave mirror of focal length 0.2 m when silvered from its plane surface. The refractive index of the material of the lens is 1.5. The radius of curvature of the convex surface of the lens will be
0.1 m
0.75 m
0.4 m
0.2 m
The refractive index of a particular material is 1.67 for blue light, 1.65 for yellow light and 1.63 for red light. The dispersive power of the material is
0.031
1.60
0.0615
0.024
Rainbow is formed due to
total internal reflection
scattering
refraction
dispersion and total internal reflection
A beam of parallel rays is brought to focus by a plano-convex lens. A thin concave lens of the same focal length is joined to the first lens. The effect of this is
the focus shifts to infinity
the focal point shifts towards the lens by a small distance
the focal point shifts away from the lens by a small distance
the focus remains undisturbed
Which mirror is to be used to obtain a parallel beam of light from a small lamp ?
Plane mirror
Convex mirror
Concave mirror
Any one of these
Which of the following is a wrong statement ?
D = 1/f where f is the focal length and D is called the refractive power of a lens
Power is expressed in a diopter when f is in metres
Power is expressed in diopter and does not depend on the system of unit used to measure f
D is positive for convergent lens and negative for divergent lens
C.
Power is expressed in diopter and does not depend on the system of unit used to measure f
Power is expressed in diopter and depends on the system of unit used to measure f.
Identify the wrong description of the above figures :
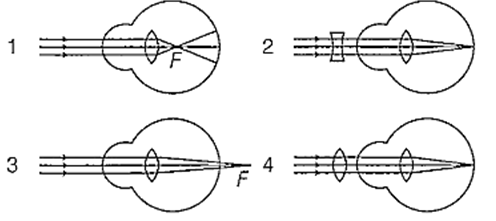
1 represents far-sightedness
2 correction for short sightedness
3 represents far-sightedness
4 correction for far-sightedness
The wave theory of light, in its original form, was first postulated by
Isaac Newton
Chnstian Huygens
Thomas Young
Augustin Jean Fresnel
At Kavalur in India, the astronomers using a telescope whose objective had a diameter of 1 m started using telescope of diameter 2.54 m. This resulted in
the increase in the resolvmg power by 2.54 times for the same λ.
the increase in the limiting angle by 2.54 times for the same λ.
decrease in the resolving power
no effect on the limiting angle
The twinkling effect of star light is due to
total internal reflection
high dense matter of star
constant burning of hydrogen in the star
the fluctuating apparent position of the star being slightly different from the actual position of the star
