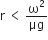Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsThe moment of inertia of a thin uniform rod of mass M and length L about an axis passing through its mid - point and perpendicular to its length is Io. Its moment of inertia about an axis passing through one of its ends and perpendicular to its length is
Io + ML2/4
Io + 2ML2
Io + ML2
Io + ML2
A body of mass M hits normally a rigid wall with velocity v and bounces back with the same velocity. The impulse experienced by the body is
1.5 Mv
2 Mv
zero
zero
An automobile moves on a road with a speed of 54 km h-1. The radius of its wheels is 0.45 m and the moment of inertia of the wheel about its axis of rotation is 3 kg m2 . If the vehicle is brought to rest in 15 s, the magnitude of average torque transmitted by its breaks to the wheel is
6.66 kg m2s-2
8.58 kg m2s-2
10.86 kg m2s-2
10.86 kg m2s-2
A.
6.66 kg m2s-2
As velocity of an automobile vehicle
 The value of α for which angular momentum about origin is conserved is
The value of α for which angular momentum about origin is conserved is
-1
2
zero
zero
Point masses m1 and m2 are placed at the opposite ends of a rigid rod of length L and negligible mass. The rod of length L and negligible mass. The rod is to be set rotating about an axis perpendicular to it. The position of point P on this rod through which the axis should pass so that the work required to set the rod rotating with angular velocity ω0 is minimum is given by

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
A rectangular coil of length 0.12 m and width 0.1 m having turns of wire is suspended vertically in a uniform magnetic field of strength 0.2 Wb/m2.The coil carries a current of 2 A. If the plane of the coil is inclined at an angle of 30o with the direction of the field, the torque required to keep the coil in stable equilibrium will be
0.15 Nm
0.20 Nm
0.24 Nm
0.24 Nm
A coil has resistance 30 O and inductive reactance 20 O at 50 Hz frequency. If an AC source 200 V, 100 Hz, is connected across the coil, the current in the coil will be
4.0 A
8.0 A


A small mass attached to a string rotats on frictionless table top as shown. If the tension is the string is increased by pulling the string causing the radius of the circular motion to decrease by a factor of 2, the kinetic energy of the mass will
remain constant
increase by a factor of 2
increase by a factor 4
increase by a factor 4
A circular disk of moment of inertia It is rotating in a horizontal plane, about its symmetry axis, with a constant angular speed. Another disk of moment of inertia Ib is dropped coaxially onto the rotating disk. Initially, the second disk has zero angular speed. Eventually, both the disks rotate with constant angular speed.
Another disk of moment of inertia Ib is dropped coaxially onto the rotating disk. Initially, the second disk has zero angular speed. Eventually, both the disks rotate with constant angular speed. The energy lost by the initially rotating disc due to friction is
The energy lost by the initially rotating disc due to friction is
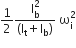
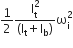
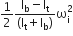
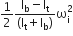
A gramophone record is revolving with an angular velocity ω. A coin is placed at a distance r from the centre of the record. The static coefficient of friction is μ. The coin will revolve with the record if
r = μgω2