 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice Questions|
LIST I (Aspect) |
LIST II (Diagram) |
| (a) Rural and Urban Population | (i) Comparative Bars |
| (b) Population density | (ii) Isolines |
| (c) Relative relief | (iii) Dots and spheres |
| (d) Decadal population | (iv) Choropleth |
a-iv , b-iii , c-i , d-ii
a-i , b-ii , c-iii , d-iv
a-ii , b-i , c-iv , d-iii
a-iii , b-iv , c-ii , d-i
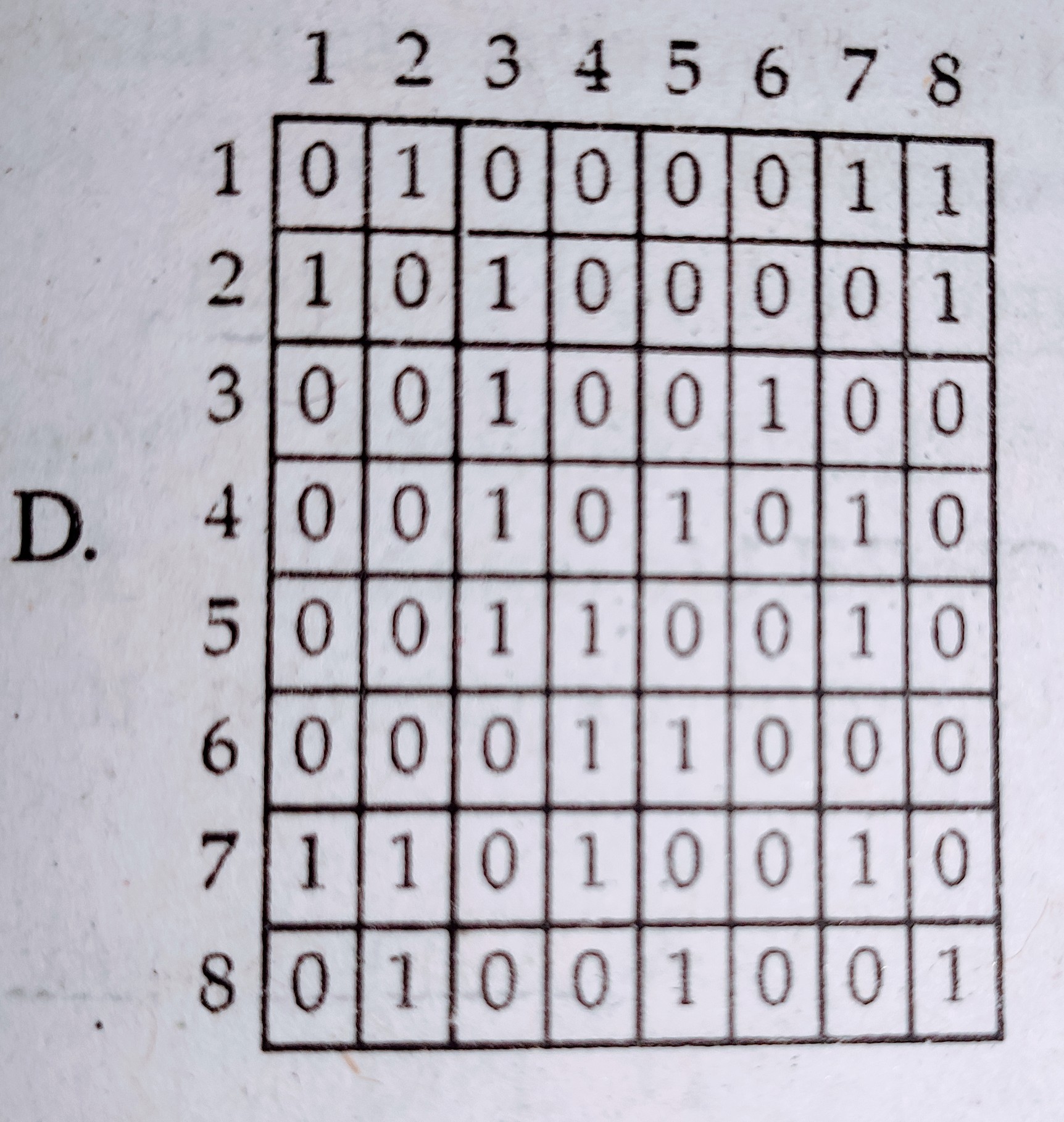
Consider the following road network diagram of an area :
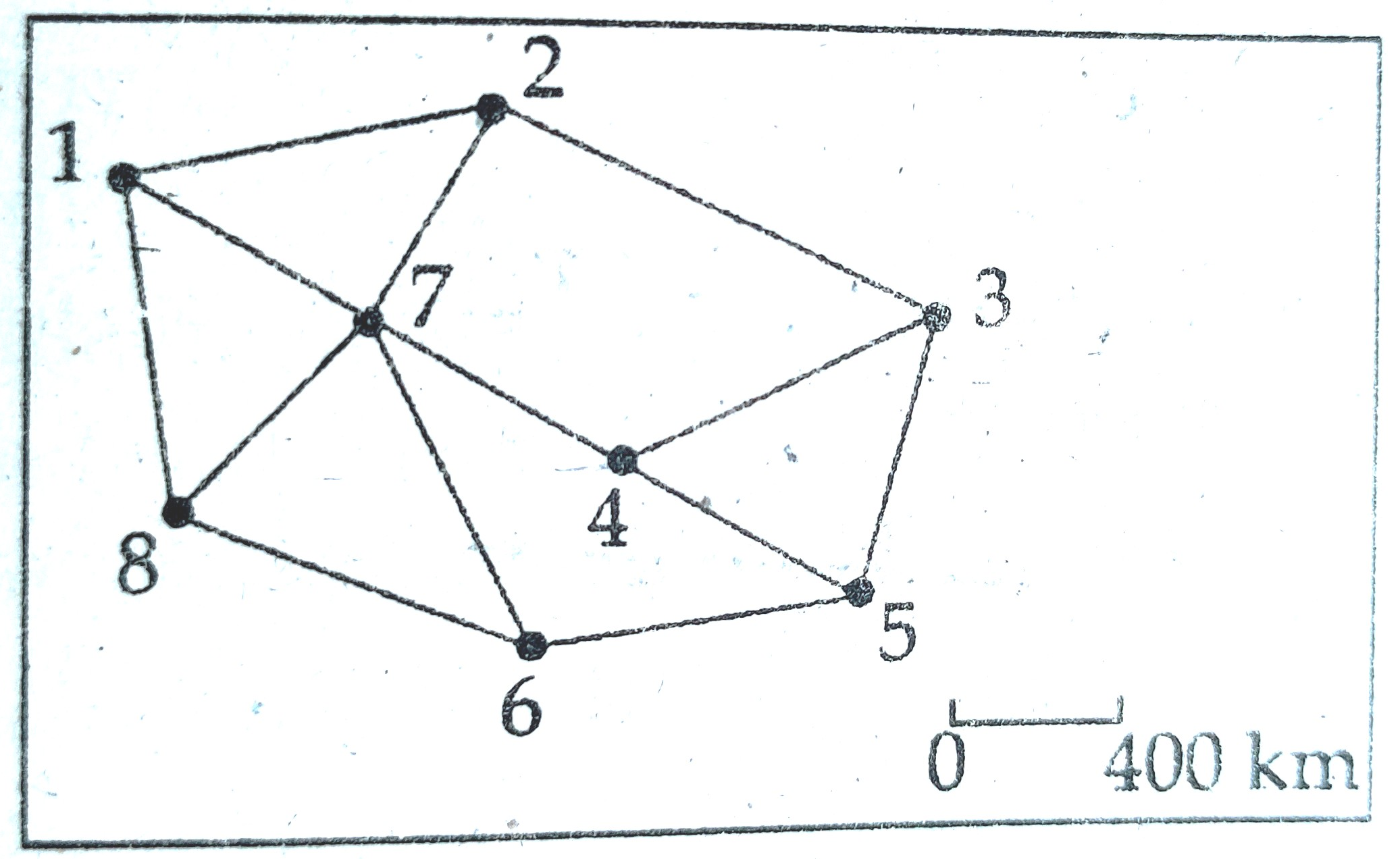
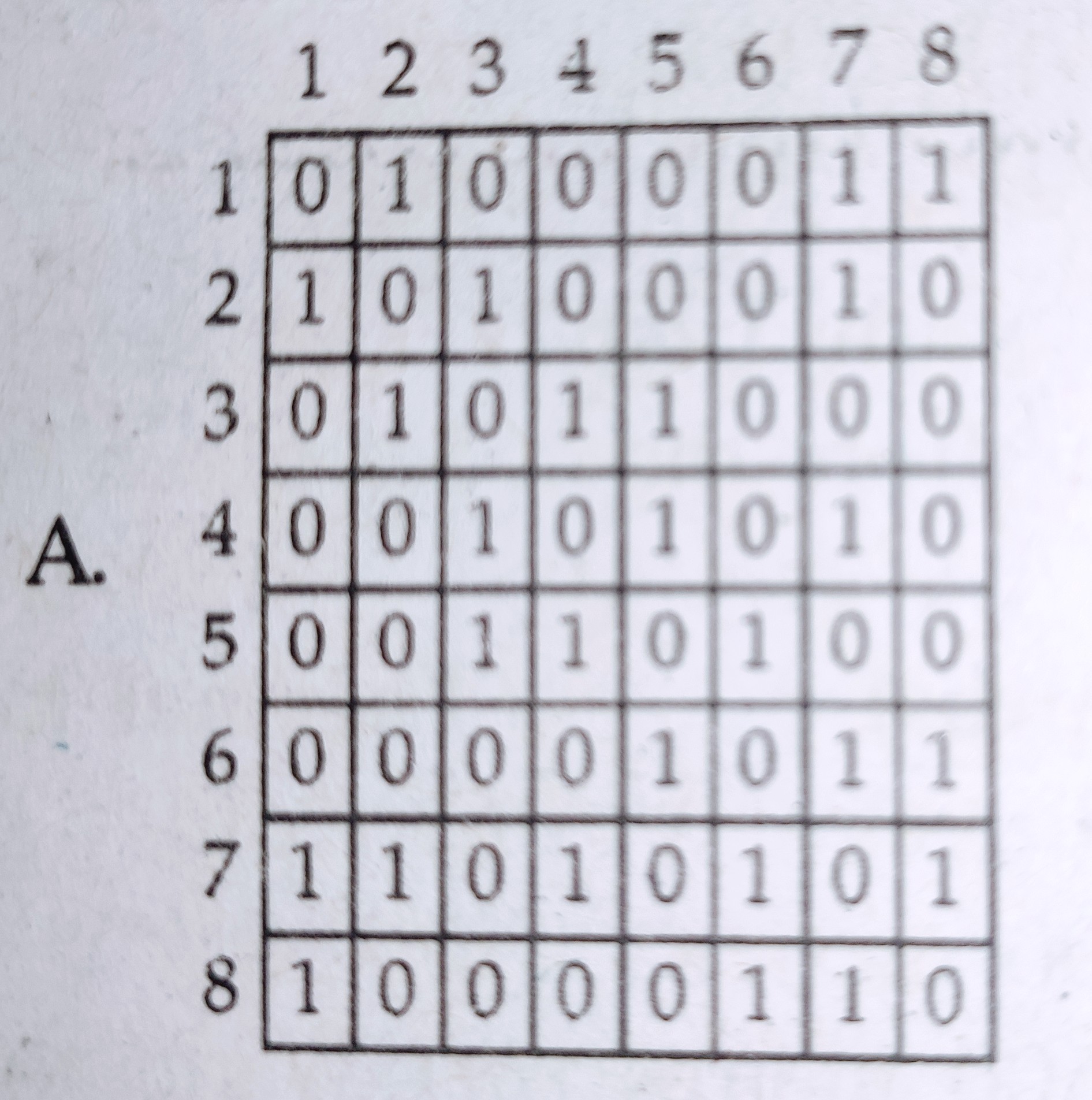
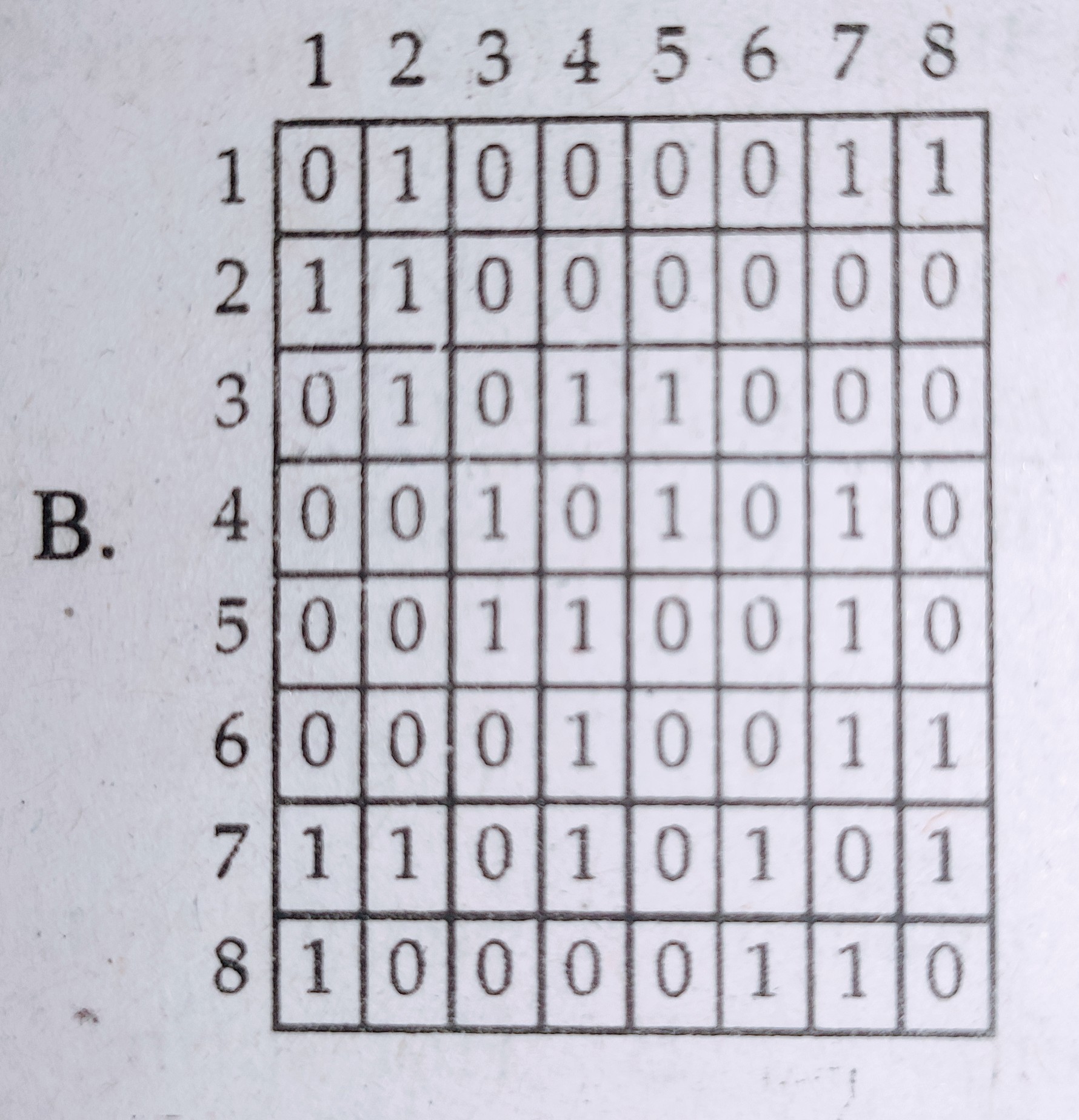
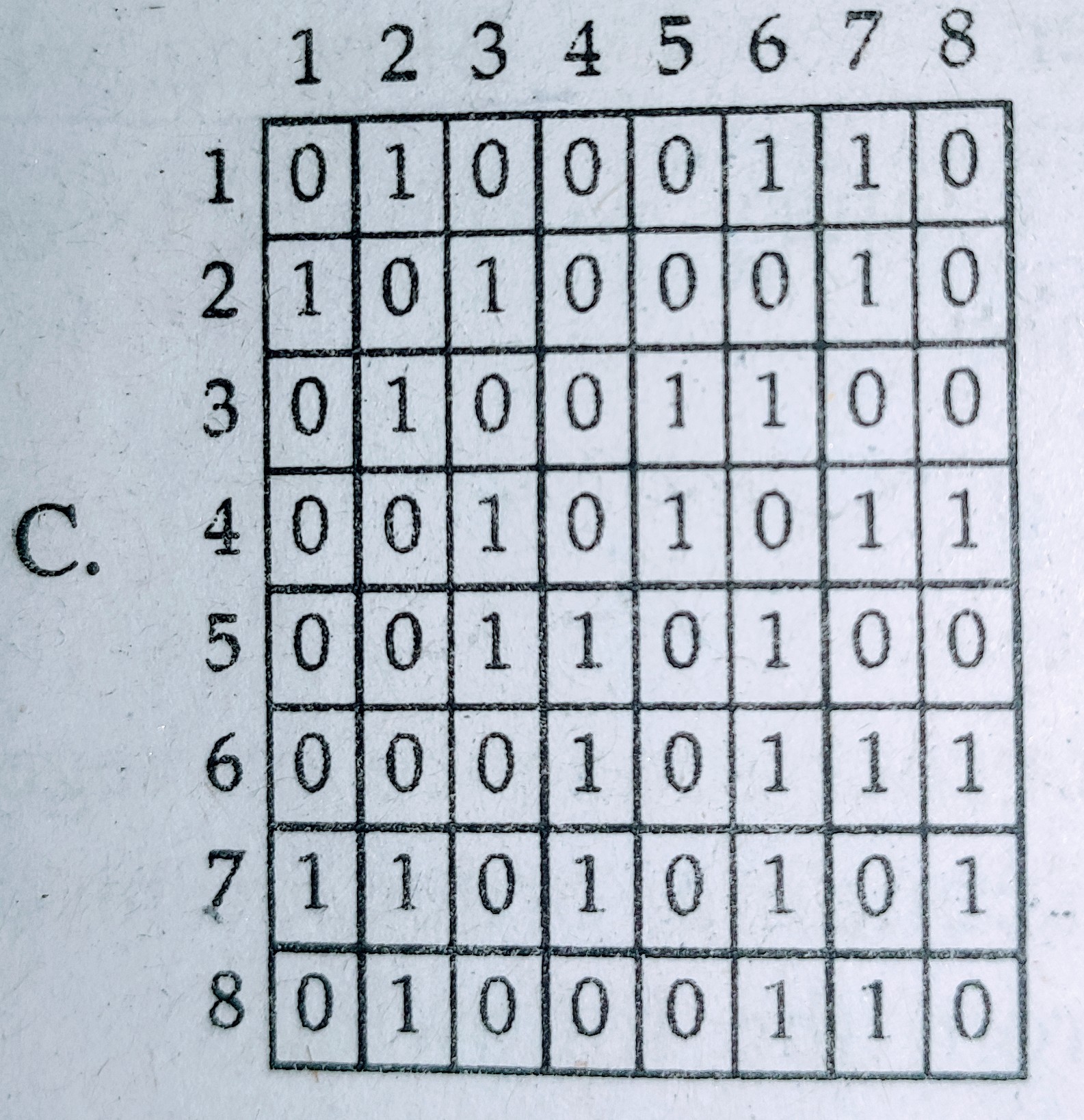
Select the correct connectivity matrix for the above network :
Which one of the following authors suggested a fivefold divisions of adopters on the basis of the time lag between receiving and acting upon new information as shown in diagram below ?
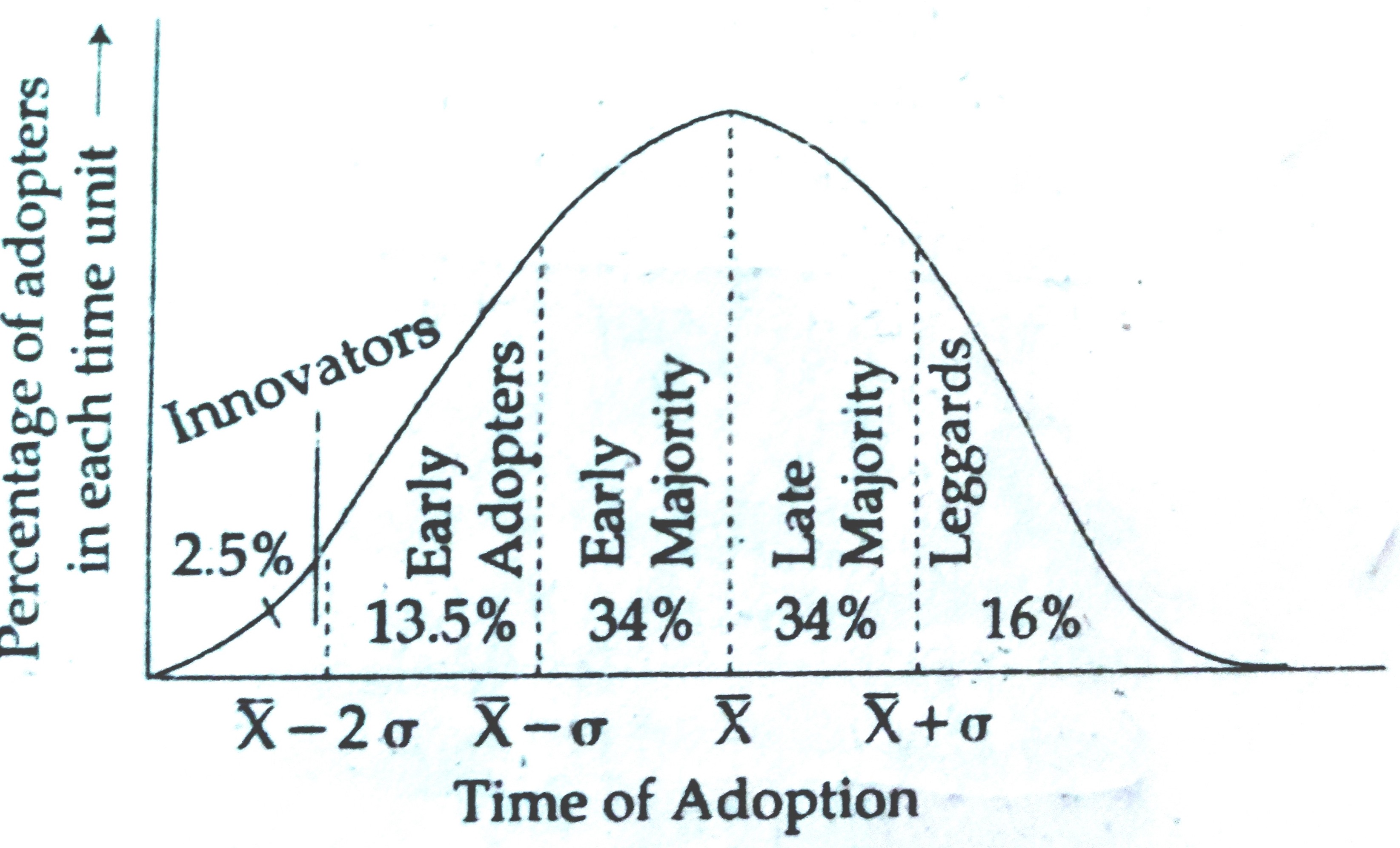
E.M . Rogers
L.W. Bowden
Z. Giriliches
T. Haggerstrand
Which one of the following is correct ?
Arithmetic mean is a numeric value
Arithmetic mean is not affected by the variability in the data sets
Arithmetic mean is always a positive number
Arithmetic mean is notn useful for any further statistical analysis of the the data
A.
Arithmetic mean is a numeric value
Which one of the following central tendencies is the appropriate method for the study of dispersion ?
Arithmetic Mean
Median
Mode
Geometric mean
Which one of the following cartographic techniques is suitable for measuring spatial association among different attributes of the regional economy ?
Bar diagram
Pie diagram
Choropleth
Isopleth
| LIST I | LIST II |
| (a) Isopleth | (i) Natural grouping |
| (b) Dot maps | (ii) Distribution of population |
| (c) Scatter diagrams | (iii) Wind direction |
| (d) Star diagrams | (iv) Changes which are relatively gradual |
a-iv , b-ii , c-iii , d-i
a-ii , b-iv , c-iii , d-i
a-iv , b-ii , c-i , d-iii
a-ii , b-iv , c-i , d-iii
Spatial data is tored in computer by using :
Plotter digitizer and keyboard
Keyboard and plotter
Scanner , digitizer and keyboard
Digitizer and scanner
LANDSAT , SPOT and IRS are examples of :
Sun-synchronous satellites
Geostationary satellites
Radars
Natural satellites
Which one of the following statistical method is best suited for groundwater exploration by using GIS tools ?
Stanadard deviation method
Principal component analysis method
Trial and error method
Index - overlay method
