 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsThe most appropriate sampling technique to represent the heterogenous population of a region is :
Cluster
Random stratified
Systematic
Purposive
|
LIST I (Statistics) |
LIST II (Analysis) |
| (a) Standard Distance | (i) Principal component |
| (b) Nearest Neighbour | (ii) Scatter Diagram |
| (c) Correlation | (iii) Settlement pattern |
| (d) Eigen Value | (iv) Centrographic measure |
a-iii , b-iv , c-i , d-ii
a-iv , b-iii , c-ii , d-i
a-i , b-iv , c-iii , d-ii
a-ii , b-iii , c-iv , d-i
Consider the following figures as X AND Y respectively :
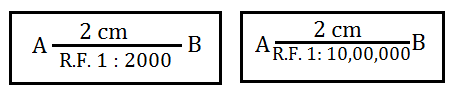
Fig X is small scale and the distnce between A and B is 40 metres
Fig Y is large scale and the distnce between C and D is 4 km
Fig X is large scale and Fig Y is small scale. The distance between A and B and C and D are 40 metres and 20 km respectively.
Fig X is alrge scale and Fig Y is small scale . The distance between A & B and C & D are equal.
If the variability of rainfall is to be measured , which of the following techniques will be used ?
Mean Deviation
Standard Deviation
Co-efficient of Variation
Interquartile Range
Which of the following is not a Quantitative Distribution Map ?
Choroschematic Map
Isopleth Map
Dot Map
Choropleth Map
Occupational structure of population in India at state level is best represented by :
Dot Method
Isopleth
Choropleth
Pie Diagram
In which of the following year , IRS-IA was launched
1982
1987
1988
1990
C.
1988
Which one of the following values of correlation coefficient (r) is not correctly matched degree of relationship ?
+ 0.99 High
+ 0.50 Moderate
- 0.01 Very Low
- 0.99 Nil
An original map has the R.F. - 1/50000 and RF of the new map will be 1/250000. What is the correct proportion of enlargement/reduction as given below ?
Reduction 1/5
Enlargement (5 times)
Reduction 1/10
Enlargement (10 times)
ASSERTION (A) : The Raster format data structure provides a greater computional efficiency.
REASON (R) : The raster data is simple.
Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) explains (A).
Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) does not explains (A).
(A) is correct , but (R) is false.
(A) is false , but (R) is correct.
