 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice Questions|
LIST I (Distribution of Settlements) |
LIST II (Pattern) |
(a) 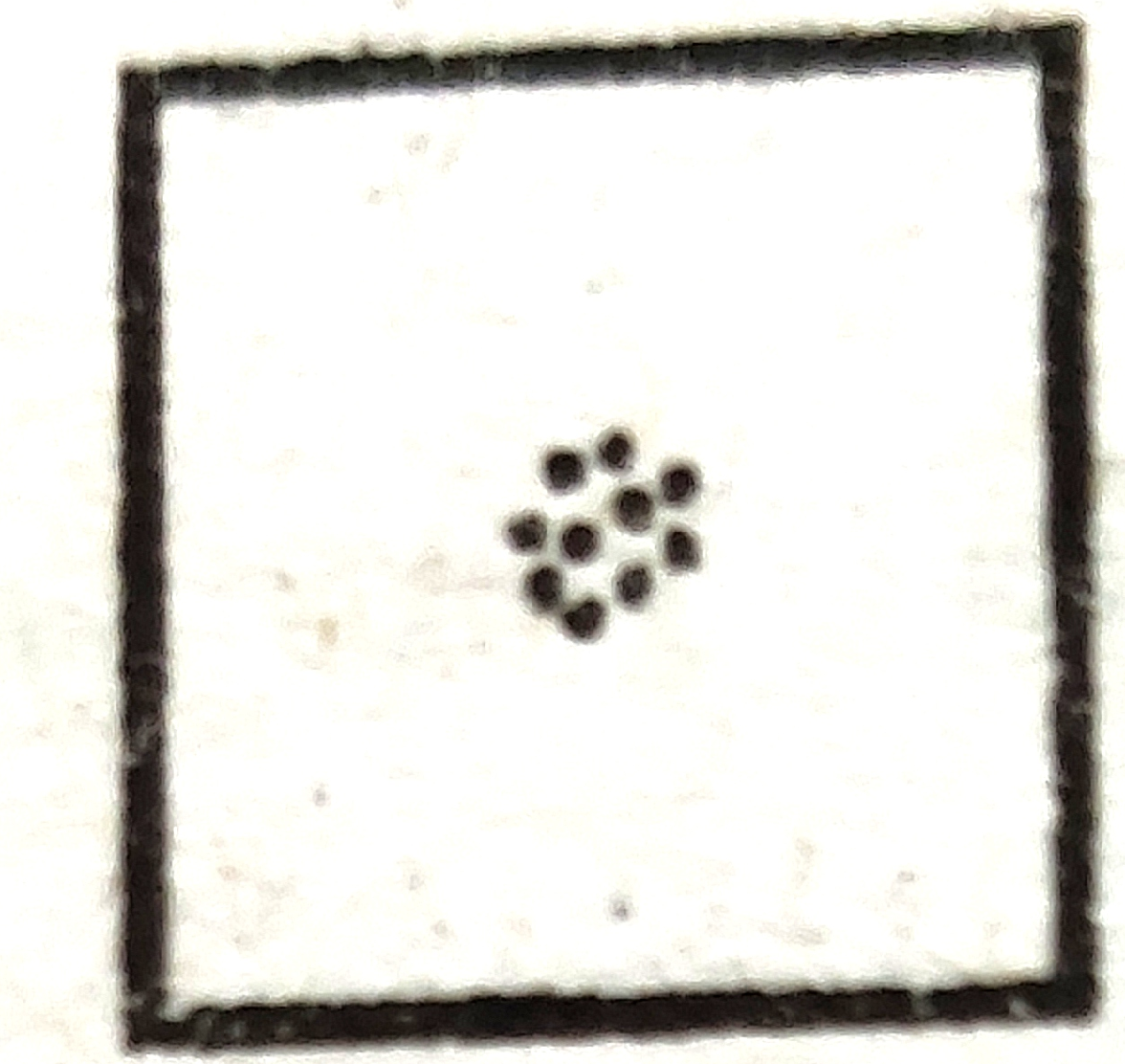 |
(1) Perfect Uniform |
(b)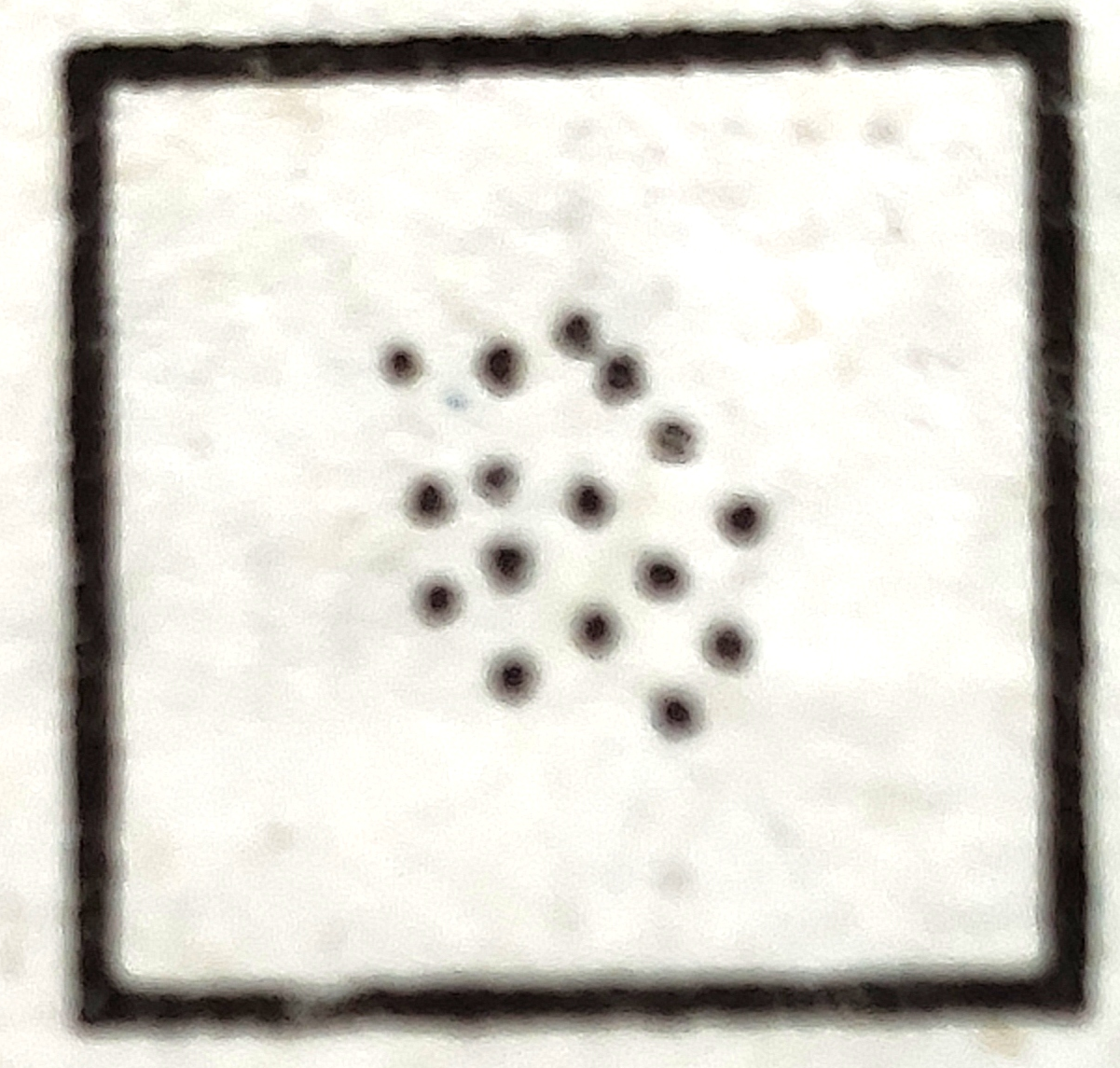  |
(2) Cluster |
(c) 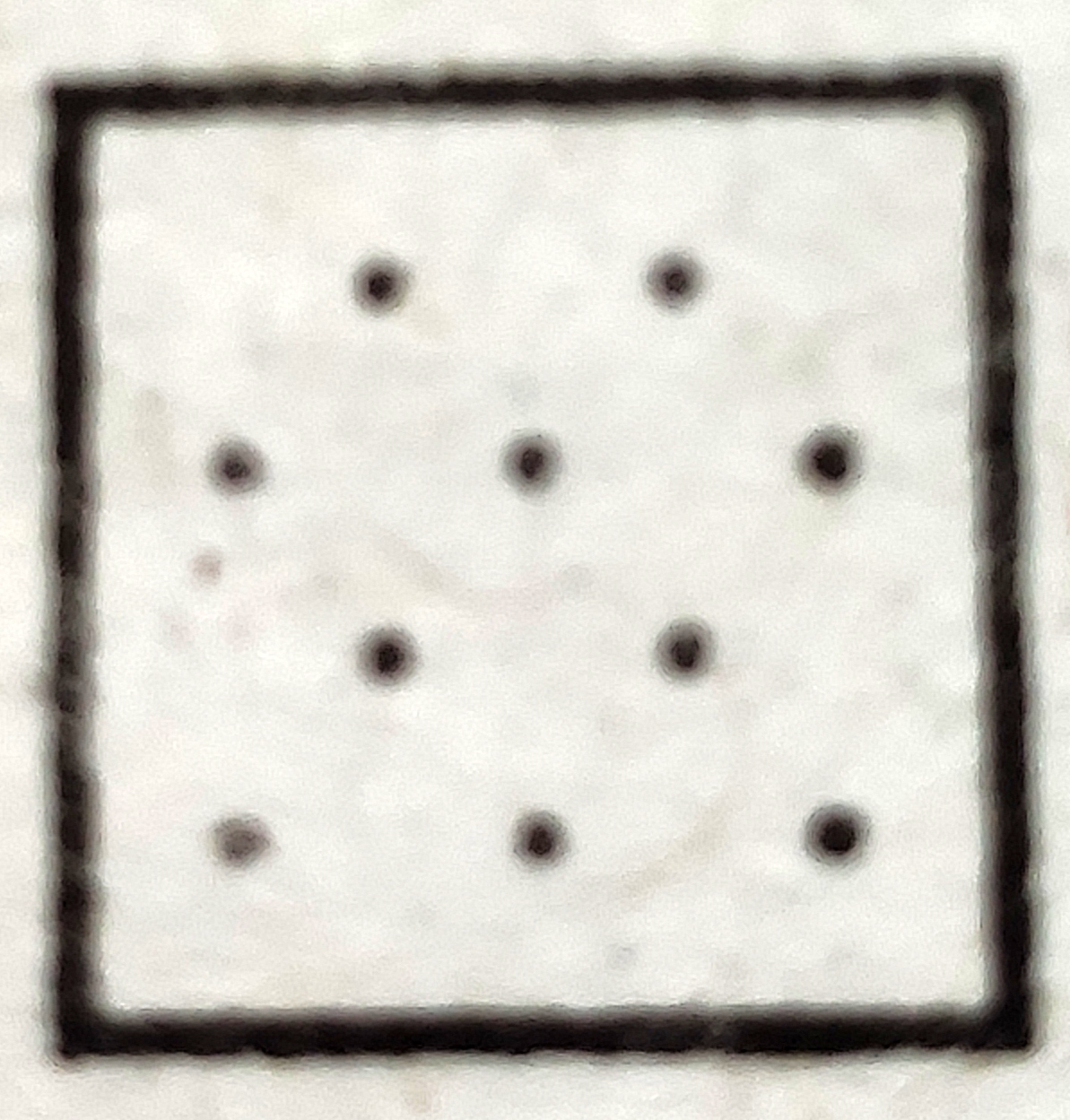 |
(3) Random |
(d) 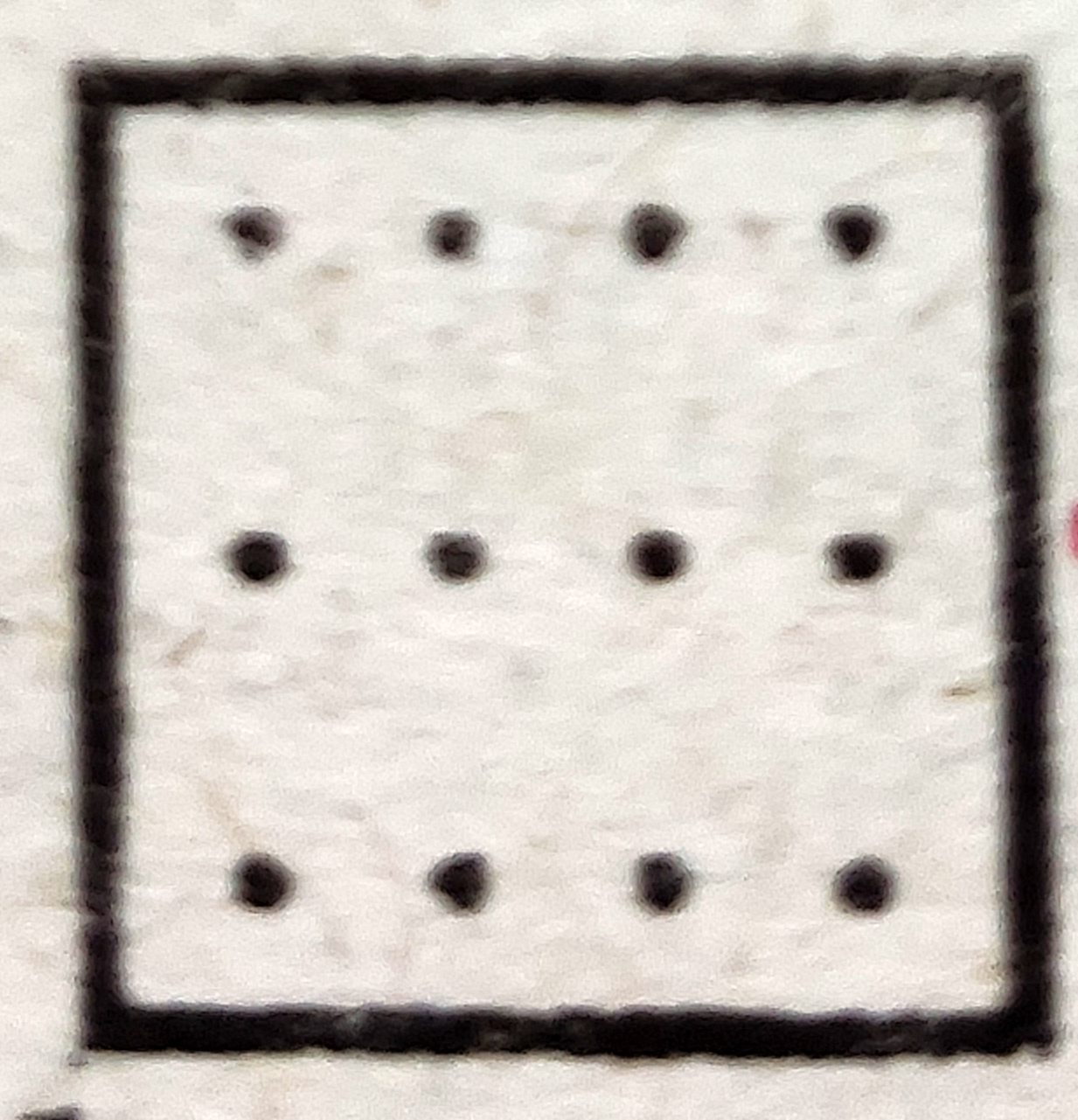 |
(4) Uniform |
a-2 , b-3 , c-1 , d-4
a-2 , b-3 , c-4 , d-1
a-2 , b-1 , c-4 , d-3
a-1 , b-2 , c-3 , d-4
ASSERTION (A) : Urbanization is a defining phenomenon of this century and the developing countries are at the focus of this transformation.
REASON (R) : The urban shift has happened in the last few decades largely due to rapid growth of mega cities in the developing countries.
Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(A) is true , but (R) is false.
(A) is false , but (R) is true.
Edward L. Ullman's 1957 study on commodity flows to study spatial interaction and regional economic structure was based on economy of which country ?
Europe
U.S.A
U.K.
Australia
B.
U.S.A
|
LIST I (Geographers) |
LIST II (Theories/Model/Concepts) |
| (a) J. Gottman | (1) Concentric zone theory |
| (b) E. Burgess | (2) Primate city |
| (c) M. Jefferson | (3) Multiple Nuclei model |
| (d) C. Harris and E. Ullman | (4) Megalopolis |
a-1 , b-4 , c-3 , d-2
a-2 , b-1 , c-4 , d-3
a-3 , b-2 , c-1 , d-4
a-4 , b-1 , c-2 , d-3
|
LIST I (Year) |
LIST II (Books) |
| (a) 1826 | (1) Theory of the Location of Industries |
| (b) 1966 | (2) The EConomies of the Location |
| (c) 1954 | (3) The Isolated State |
| (d) 1909 | (4) Central Places in Southern Germany |
a-1 , b-3 , c-2 , d-4
a-3 , b-2 , c-1 , d-4
a-3 , b-4 , c-2 , d-1
a-2 , b-4 , c-3 , d-1
Which one of the following is not in conformity with the central place theory ?
Central place is a settlement providing services for the population of its better land.
Hierarchy and nesting pattern results in maximum number of central places.
Ubiquities and localized raw materials
Market areas for different goods resemble nets of hexagons
|
LIST I (Concepts) |
LIST II (Definitions) |
| (a) Continuum Urban Areas | (1) Groups of towns of decreasing but approximately equal size and importance. |
| (b) Losch Model | (2) Relationship between the largest city and second largest city. |
| (c) Urban Hierachy | (3) Various hexagonal systems operate at diferent levels and are superimposed on each other. |
| (d) Primate City | (4) Gradual and continuos decrease of urban population size with decreasing rank. |
a-4 , b-3 , c-1 , d-2
a-2 , b-1 , c-3 , d-4
a-3 , b-2 , c-4 , d-1
a-1 , b-4 , c-2 , d-3
|
LIST I (Type of Village) |
LIST II (Definitions) |
| (a) Green village | (1) Villages which have developed at an inter-section of roads. |
| (b) Cruciform village | (2) With houses and church clustered around a small village green. |
| (c) Disperesed village | (3) Found along routeways or where conditions have impeded a lateral development of the settlements. |
| (d) Street village | (4) Isolated farms are scattered irregularly throughout countryside. |
a-3 , b-2 , c-1 , d-4
a-2 , b-3 , c-4 , d-1
a-1 , b-2 , c-3 , d-4
a-2 , b-1 , c-4 , d-3
In which year , M. Jefferson examined the size relationship between the primate city and next largest cities in a study entitled "The Law of the Primate City" ?
1938
1937
1936
1939
Which one oft he following authors identified three basic factors affecting interaction between regions : Complementarily , intervening opportunity and transferability ?
P.R. White
H.L. Gauthier
E . Taafe
E.L. Ullman
