 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsThe compound which gives turbidity immediately with Lucas reagent at room temperature is
butan-1-ol
butan-2-ol
2-methyl propan-2-ol
2-methyl propan-1-ol
The conversion of m-nitrophenol to resorcinol involves respectively
hydrolysis, diazotization and reduction
diazotization, reduction and hydrolysis
hydrolysis, reduction and diazotization
reduction, diazotization and hydrolysis
HCHO was treated with a reagent X. The product formed upon hydrolysis in the presence of an acid gave C2H5OH. The reagent X is
alcoholic KOH
alcoholic KCN
CH3MgI
aqueous KOH
Which one of the following is not formed when a mixture of methyl bromide and bromobenzene is heated with sodium metal in the presence of dry ether?
diphenyl
propane
toulene
ethane
Power alcohol is a mixture of
80% petrol + 20% ethanol + small quantity of benzene
80% ethanol + 20% benzene + small quantity of petrol
50% Petrol + 50% ethanol + small quantity of benzene
80% petrol + 20% benzene + small quantity of ethanol
Which of the following is strongly acidic?
Phenol
o-cresol
p-nitrophenol
p-cresol
C.
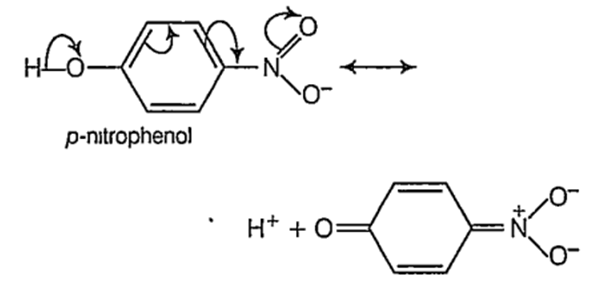
p-nitrophenol
The acidity of phenols ts due to the greater resonance stabilization of the phenoxide ion relative to phenol. Therefore, electron withdrawing groups (EWG) like - NO2 which stabilize the phenoxide ion more by dispersing the negative charge will tend to increase the acidity of phenols.
On the other hand, electron donating groups (EDG) like-alkyl group destabilize the phenoxide ion by intensifying the negative charge relative to phenol tend to decrease the acidic strength of phenols.
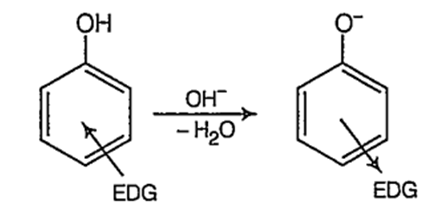
As methyl group has + / effect and it is stronger at o-position than at p-position, (+ I effect decreases with distance) o-cresol is a weaker acid than p-cresol. Thus, the order of acidic strength.
p- nitrophenol > phenol > p- resol > o-cresol
When CH2=CH-O-CH2-CH3 reacts with one mole of HI, one of the products formed is
ethane
ethanol
iodoethene
ethanal
0.44 g of a monohydric alcohol when added to methylmagnesium iodide in ether liberates at STP, 112 cm3 of methane. With PCC the same alcohol forms a carbonyl compound that answers silver mirror test. The monohydric alcohol is
H3C-CH(OH)-CH2-CH3
(CH3)3C-CH2OH
H3C-CH(OH)-CH2-CH2-CH3
(CH3)2CH-CH2OH
