 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsA short linear object, of length l, lies along the axis of a concave mirror, of focal length f, at a distance d from the pole of the mirror. The size of the image is then (nearly)
Assertion: A total reflecting prism is used to erect the inverted image without deviation.
Reason: Rays of light incident parallel to base of prism emerge out as parallel rays.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false.
Assertion: The edges of the images of white object formed by a concave mirror on the screen appear white.
Reason: Concave mirror does not suffer chromatic aberration.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false
A coverging lens forms a real image I of an object on its principal axis. A rectangular slab of refractive index and thickness x is introduced between l and the lens, I will move
towards the lens ( μ - 1 ) x
towards the lens by x
away from the lens by (μ - 1 ) x
away from the lens by x
When white light passes through a prism, the deviation is maximum for
violet light
green light
red light
yellow light
A.
violet light
Wavelength is inversely proportional to the deviation in the path of the light. Red light suffers the least amount of deviation and violet the most.
Since the wavelength of violet light is the smallest, therefore maximum deviation will occur for violet light.
An object 5 cm tall is placed 1 m from a concave spherical mirror which has a radius of curvature of 20 cm. The size of the image is
0.11 cm
0.50 cm
0.55 cm
0.60 cm
The magnifying power of a compound microscope increase with
the focal length of objective lens is increased and that of eye lens is decreased
the focal length of eye lens is increased and that of objective lens is decreased
focal lengths of both objects and eye-piece are increased
focal lengths of both object and eye-piece
A thread is tied slightly loose to a wire frame as in figure and the frame is dropped into a soap solution and taken out. The frame is completely covered with the film. When the portion A is punctured with a pin, the thread
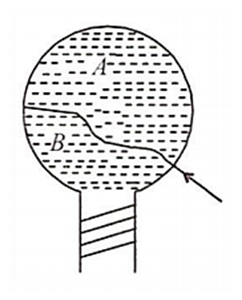
become concave towards A
become convex toward A
either (a) or (b) depending on the size of A with respect to B
remains in the initial position
Assertion: The colour of the green flower seen through red glass appears to be dark
Reason: Red glass transmits only red light.
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false
Assertion: A double convex lens ( μ = 1.5 ) has focal length 10 cm. When the lens is immersed in water ( μ = 4/3 ) its focal length becomes 77 cm.
Reason:
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
If assertion is true but reason is false
If both assertion and reason are false
