 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type(a) Name the enzyme responsible for the transcription of tRNA and the amino acid the initiator tRNA gets linked with.
(b) Explain the role of initiator tRNA in initiation of protein synthesis.
Name the two different categories of microbes naturally occurring in sewage water. Explain their role in cleaning sewage water into usable water.
Write the function of each one of the following:
(a) (Oviducal) Fimbriae
(b) Coleoptile
(c) OxytocinName the genes responsible for making Bt cotton plants resistant to bollworm attack. How do such plants attain resistance against bollworm attacks? Explain.
Study a part of the life cycle of malarial parasite given below. Answer the questions that follow: 
(a) Mention the roles of A in the life cycle of the malarial parasite.
(b) Name the event C and the organ where this event occurs.
(c) Identify the organ B and name the cells being released from it.Given below is the representation of amino acid composition not the relevant translated portion of β-chain of hemoglobin, related to the shape of human red blood cells. 
(a) Is this representation indicating a normal human or a sufferer from certain related genetic disease? Give reason in support of your answer.
(b) What difference would be noticed in the phenotype of the normal and the sufferer related to this gene?
(c) Who are likely to suffer more from the defect related to the gene represented the males, the females or both males and females equally? And why?By the end of 2002 the public transport of Delhi switched over to a new fuel. Name the fuel. Why is this fuel considered better? Explain.
Draw a schematic sketch of pBR 322 plasmid and label the following in it:
(a) Any two restriction sites.
(b) Ori and rop genes.
(c) An antibiotic resistant gene.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeExplain the carbon cycle with the help of a simplified model.
Key process involved in carbon cycle is photosynthesis and respiration.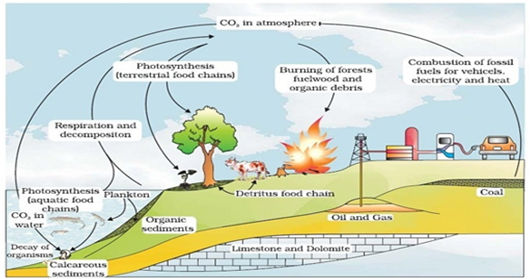
Carbon cycling occurs through atmosphere, ocean and through living and dead organisms.
1. Carbon is fixed during photosynthesis by the plants.
2. A large amount of carbon is returned to the atmosphere as CO2 by the respiratory activities of organisms.
3. Decomposers also contribute substantially to the CO2 by acting on waste materials and dead organic matters.
4. Some of the fixed carbon is lost to the sediments and removed from the circulation.
5. Burning of fossil fuels forest fire and combustion of organic matter volcanic activity also release CO2 in the atmosphere.
