 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type(a) Why does the presence of an excess of lithium make LiCl crystals pink?
(b) A solid with cubic crystal is made of two elements P and Q. Atoms of Q are at the corners of the cube and P at the body-center. What is the formula of the compound?
(a) When crystals of LiCl is heated in presence of excess of lithium, Cl- ions from crystal diffuse on the surface and combine with ionized Li to form LiCl. The released unpaired electrons occupy the anionic sites known as F-centers. The pink colour results by excitation of these electrons when they absorb energy from visible light falling on them.
(b) It is given that the atoms of Q are present at the corners of the cube. Therefore, number of atoms of Q in one unit cell =
Also, it is also given that the atoms of P are present at the body-center.
Therefore, number of atoms of P in one unit cell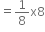 = 1
= 1
This means that the ratio of the number of P atoms to the number of Q atoms, P: Q = 1:1
Hence, the formula of the compound is PQ.
How are interhalogen compounds formed? What general compositions can be assigned to them?
Aluminum crystallizes in an fcc structure. Atomic radius of the metal is 125 pm. What is the length of the side of the unit cell of the metal?
The standard electrode potential (E°) for Daniell cell is +1·1 V. Calculate the G° for the reaction
Zn(s) + Cu2+ (aq) ----> Zn+ (aq) + Cu (s)
(1 F = 96500 C mol-1).
(a) For a reaction A + B --> P, the rate law is given by,
r = k [A]1/2 [B]2.
What is the order of this reaction?
(b) A first order reaction is found to have a rate constant k = 5·5 x 10-14 s-1. Find the half-life of the reaction.
Outline the principles of refining of metals by the following methods:
(i) Zone refining
(ii) Vapour phase refining
Define the following terms giving an example of each:
(i) Associated colloids
(ii) Lyophilic sol
(iii) Adsorption
