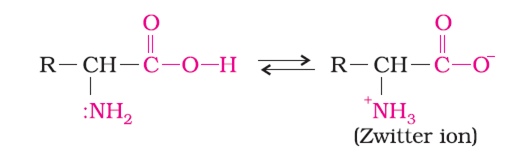Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type(A), (B) and (C) are three non-cyclic functional isomers of a carbonyl compound with molecular formula C4H8O .
Isomers (A) and (C) give positive Tollen’s test whereas isomer (B) does not give Tollen’s test but gives positive Iodoform test. Isomers (A) and (B) on reduction with Zn(Hg)/conc. HCl give the same product (D).
(a) Write the structures of (A), (B), (C) and (D)
(b) Out of (A), (B) and (C) isomers, which one is least reactive towards addition of HCN ?
Write the structure of the product when chlorobenzene is treated with methyl chloride in the presence of sodium metal and dry ether.
Write the structure of the alkene formed by dehydrohalogenation of 1-bromo-1-methylcyclohexane with alcoholic KOH.
Amino acids show amphoteric behaviour. Why?
In aqueous solution, the carboxyl group of an amino acid can lose a proton and the amino group can accept a proton to give a dipolar ion known as zwitter ion.
Therefore, in zwitter ionic form, the amino acid can act both as an acid and as a base. Thus, amino acids show amphoteric behaviour.