 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeWrite balanced equations for the following reactions:
Chlorine is passed into an aqueous solution of sulphur dioxide.
Write balanced equations for the following reactions:
Aluminium powder is warmed with hot and concentrated caustic soda solution.
Write balanced equations for the following reactions:
Concentrated nitric acid is added to copper turnings kept in a beaker.
Write balanced equations for the following reactions:
Red lead (trilead tetroxide) is warmed with concentrated hydrochloric acid.
Write balanced equations for the following reactions:
Chlorine gas is passed through an aqueous solution of Iron (II) sulphate acidified with dilute sulphuric acid.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type
When heated, potassium permanganate decomposes according to the following equation:
i) some potassium permanganate was heated in a test tube. After collecting one litre of oxygen at room temperature, it was found that the test tube had undergone a loss in mass of 1.32g. If one litre of hydrogen under the same conditions of temperature and pressure has a mass of 0.0825g, calculate the relative molecular mass of oxygen.
ii) Given that the molecular mass of potassium permanganate is 158, what volume of oxygen (measured at room temperature) would be obtained by the complete decomposition of 15.8 g of potassium permanganate? ( Molar volume at room temperature is 24 litres.)
i) Loss of weight of due to formation of O2
the weight of 1 litre of oxygen under room conditions = 1.32g
the weight of 1 litre of hydrogen under room conditions = 0.0825 g
Now according to Avogadro's law under similar conditions of temperature and pressure equal volumes of gases contain equal number of moles
Suppose, 1 litre of oxygen under room condition contain n molecules.
Therefore,
Relative molecular mass of oxygen =
[therefore, atom of hydrogen = 1/2 molecules of hydrogen]
= 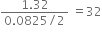
ii) 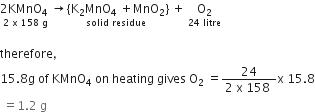
Sodium hydroxide solution is added first in a small quantity, then in excess to the aqueous salt solution of copper (II) sulphate,Zinc, lead nitrate, Calcium chloride and iron(III) sulphates. Copy the following table and write the colour of the precipitate in (i) to (v) and the nature of the precipitate (soluble or insoluble ) in (vi) to (x).
|
Aqueous salt solution |
Colour of precipitate when NaOH is added in a small quantity |
Nature of precipitate (soluble or insoluble) when NaOH is added in excess. |
|
Copper (II) sulphate |
(i) |
(vi) |
|
Zinc nitrate |
(ii) |
(vii) |
|
Lead nitrate |
(iii) |
(Viii) |
|
Calcium chloride |
(iv) |
(ix) |
|
Iron (III) sulphate |
(v) |
(x) |
Which of the following methods,A,B,C D or E is generally used for preparing the chlorides listed below from (i) to (v). Answer by writing down the chloride and the letter pertaining to the corresponding method. Each letter is to be used only once.
A. Action of an acid on a metal.
B. Action of an acid on an oxide or carbonate
C. Direct combination
D. Neutralization of an alkali by an acid.
E. Precipitation (double decomposition)
i) Copper (II chloride)
ii) Iron (II) chloride
iii) Iron (III) chloride
iv) Lead (II) chloride
v) Sodium chloride.
