Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeDifferentiate between Apes and Man with respect to the following characteristics :
(i) Posture (ii) Cranium
(iii) Brow ridges (iv) Locomotion
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeGrowth may be defined as a more or less irreversible change in the structure, development of a cell, tissue or organism and may involve one or more of the following :
(i) increase in the amount of protoplasm.
(ii) increase in the size of cells, their number, organs and the organism as a whole.
(iii) increase in the number of cell organelles, increase in weight.
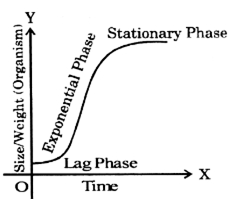
Growth Curve : Every organ of the plant body, infact every cell that the organ is composed of, shows a variation in the rate of its growth. Growth is slow in the initial stages. This is the lag phase. Now it accelerates until a maximum is reached. This is the exponential period of growth. After this the growth slows down until it comes to a standstill. This is the stationary phase.
In perennials growth continues throughout their life. But plants show a seasonal variation in growth. During, winter plant metabolism slows down and the plants become dormant. Growth is also affected by the length of day and night, the direction of light and gravity and availability or non-availability of water. On the approach of favourable climatic conditions, growth is resume. The part of the year when the plant shows maximum growth is called growing season. Duration of growth season varies with the species, climatic condition, availability of water and nutrients and the geographical location. Growth rings can be seen in the transverse section of the stem of trees. These indicate the cyclic nature of the periods of dormancy and active growth. The growth of a plant part characteristically passes through stages represented by a S-shaped (sigmoid) curve. This period is said to be grand period of growth. The curve shows that growth is very slow in the beginning, then very vast fast for sometime, and again it is slower till it stops.
There are several external and internal factors which influence growth :
External factors :
(i) Temperature
(ii) Light
(iii) Soil water content
(iv) Pollutants.
Internal factors :
Growth regulators are responsible for the development of the plant body. As development process unfolds, particular genes become involved in the synthesis of enzymes (proteins) which catalyse specific biochemical processes necessary for growth and differentiation.